Courses/Computer Science/CPSC 203/CPSC 203 Template/CPSC203 Template People/James King/Group 5
Contents
Group Members
- Sarosh Akhtar
- Johnson Kao
- Eda Libin
- Rahamatullah Siddique
- Miranda Stacey
Introduction
Mail systems and other forms of communication resulted from the need to deliver messages to people in different geographical locations. Delivering a message from one person to another has been one of mankind's greatest challenges for thousands of years.
In the beginning of time, ways of transporting messages were created by those who were in power to keep in touch with the military leaders and administrators of conquered territories. Over the ages, the benefits of secure, regular communication became increasingly important, leading us to the establishment of reliable systems of communication we have today.
Face to Face Communication
History
The roots of communication technology can be traced all the way back to 2000 B.C.
2000 B.C: Assyrian merchants used clay tablets (about the size of a pillow), which they unscripted with cuneiform characters, to send messages between towns. These messages were delivered by foot couriers, who carried half a dozen or more tablets at a time.
1700 B.C: Egyptians established a delivery system using couriers on horses that transported messages, using their writing system of hieroglyphics, across their empire (expanded into modern day Iran).
1027 B.C: China’s Chou dynasty established the imperial post, that used a combination of couriers on horseback and homing pigeons. (This system was improved by successive families, and by 1300 A.D more than 300 000 horses were based at 10 000 stations for the mail service.)
650 B.C: Babylonian Kings placed guard stations along major roads. Messages were then relayed by couriers from one station to the next. Around this time, fire beacons were introduced to deliver signals from one station to the next. (This was the first step away from face to face communication).
490 B.C: The Persian Empire greatly outnumber the Greeks, so when they landed on the plains of Marathon to expand their territory, the Greeks needed back up to defend their land. Athenian generals sent Phidippides to run to Sparta and ask for help. He ran a 140 mile, rugged course in just 36 hours to find that the Sparta’s military base would help them, but not until the moon was full due to religious laws. Phidippides then ran back to Athens to tell the Athenians that they would have to fight the Persian Army on their own. (After this, Greek couriers were often chosen due to their speed and ability to memorize the messages.)
14 A.D: Romans developed a new relay system of 80 Km per day for regular mail, and 160 Km per day for express mail.
At the close of the 4th century, communication by foot and by horseback were still being used in Europe and China. The mail service in Europe disintegrated in 410 A.D, with the collapse of the Roman Empire.
Although, we no longer have to run hundreds of miles to deliver messages to different people, the concept of face-to-face communication has not disappeared. We still physically and orally give people messages, but we have a whole new array of communication technology that makes our lives way more convenient than it was thousands of years ago.
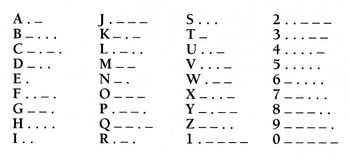
Morse Code
History
The Morse code was developed in the 1830's by Samuel Morse. Morse had quite the fascination with electricity, and the ability of wires to carry a current. He continued to learn more about these areas in hopes of developing a new means of communication. At the time, there was already a French Telegraph which was used as a method of communication, however Morse knew that by using electricity, this process could be made faster and much more efficient. This was in fact true, and eventually led to the development of the Electric Telegraph which transferred messages via electricity through wires, as well as with the help of electromagnets.
How did it work?
Once developing the actual mechanism (The Electric Telegraph) to transfer the messages, Morse then needed to identify a code for reading the messages. Firstly, in order to transfer a message, electricity would pass via wires to transfer to the telegraph on the receiving end. A pencil would be attached to the electromagnet on the receiving telegraph, and a series of dots and dashes (depending on the message sent) would be recorded on a moving slip of paper. Seeing as the message received was not written in the usual alphabet, Morse also needed to come up with a translation method for decoding the series of dots and dashes.
Originally, Morse created a numerical alphabet. The numbers 1 through 5 were symbolized by dots. The number of dots corresponded to the actual number itself. The numbers 6 through to 9 were symbolized by a series of dots and dashes. A translation dictionary was created which converted a combination of numbers into specific words. While this method was convenient at first, it began to be quite tedious attempting to decode each word by a series of numbers rather than letters. Later, Morse began working with other partners. Shortly after, they developed an easier method of sending messages. For this, series of dots and dashes now represented each letter of the alphabet, so you now just had to spell out the message, rather than translate each word.
Problems
While the Electric Telegraph and Morse code were very useful inventions for its' time, there were a few problems which developed. One of these being a problem travelling over long distances. Another major problem faced was the translation of the Morse Code into different languages. Obviously, with the current system, this was very difficult to do, so in later years, the International Morse code was created to try and rectify this problem.
Telephones/Cellphones
Telephone is an improvement and a great innovation of telegraphs which only produced “dots and dashes” when sending messages. The idea of transmitting voices electrically was proposed by Alexander Graham Bell in the 1870s, who was born in Scotland. Throughout his life, he has been finding ways to different communications, such as music was one of his talents. Hence, it was the various music tones that led him to this new proposal of producing “harmonic telegraphs”. By producing different phonetic tones, it released different frequency strengths on the electrical wires, and ultimately, it transmits different signals to the other device. The quote, “Mr. Watson, come here. I want to see you,” were the first words that were said on the new invention by Alexander Graham Bell to his personal assistant in 1876. This new invention clearly surpassed its precedent telegraphs which could only used dots and dashes to communicate.
The next voice communication technology was the invention of the cell phone. In 1973, a man named Martin Cooper, who was the former manager of Motorola tested the first cellphone. Cell phones are two-way radio devices that have "cells" which produces frequency signals for airway broadcast towers to receive. In the beginning, these airway system were built to receive limited cell phone signals in a local area. However, for convenience issue and in order to expand the cell phone market, FCC, Federal Communication Commission encourage the expansion of airways and Bell help built multiple towers to receive broader frequencies. Therefore, with multiple towers in the area, this allowed frequency signals to migrate from one tower to the next, thus increasing the transmitting efficiency as well.
Ever since the invention of these technologies, they have become a powerful tool in our everyday life. Nonetheless, the modern evolution of these devices have made them more handy and portable. Especially with cell phones, they allow people to stay in touch anywhere they go. Furthermore, with their multi-fuction features such as camera, data storage, mp3 player and GPS integrated, they've made our lives much easier and enjoyable!
Computers/Television/Video Streaming
Technology has always been an important part of life since the 19th century industrial revolution. Through the years this advances grew until we got to the most important piece of technology in today's society, the computers.
Pros for Computers
• Computers Helps to save lives(e.g. save lives in the medical field)
• Very educational when used appropriately
• Economy depends on it (stock market, banks, cash registers, etc...)
• Computers keep people connected (face book, Msn, Nexopia, etc...
• Through online resources we gain knowledge
• Computers can help us create and edit documents very easily and can help us speed up work. • Easier to communicate and send documents through computers at the push of a button
Cons for Computers
• Computers can be mean for hackers, and cyber terrorist to harm people(e.g. cleaning out someone bank account, or crashing a plain)
• Not everyone can afford it.
• Sexual predator
• It consumes time that could be put towards better use.(e.g. Students get sidetracked from homework’s).
Television set has become a common communications receiver in homes, businesses and institutions, particularly as a source of entertainment and news.
Pros for television
• It's too easy to turn it on, sit down with a bag of chips and watch it for hours.
• It might also encourage reading when a show engages you to learn more.
• Kids who watch educational show may do better in school.
Cons for television
• Too much TV. Can shrink your Knowledge.
• TV is addictive
• Things Kids learn on TV do not translate into academic success.
In the past, the only way to view a video on a computer was to first completely download the file and then play the video on the computer.Because of introduction to new technology, people can now speed up the process of viewing online videos by using streaming video. With streaming video, the video will begin to play on the computer almost the second that it begins to download and the video will continue to play as it finishes downloading onto the computer.
Pros for Video Streaming
• Instructors can place large video and audio files on the streaming media server and link them to ELMS or to another Web site.
• The streamed file cannot be downloaded to a student desktop; this makes it a good choice for audio or video files that contain copyright protected content.
• Streaming media can broadcast live events.
• Very technological
• Up to date
Cons for video streaming
• Instructors must learn to use Web DAV in order to upload files to the streaming media server.
• Students must have either the QuickTime or Real media plug-in in order to view the streamed media in their browser.
• Anyone can access to it.
• Violates privacy right.
Technology is increasing everyday in modern era and has made our lives much easier. However there are still drawbacks associated with each of the new technoligical device introduced in market. One has to be careful while making choices regarding technology by knowing about pros and cons.
Holograms: The Future
Holograms/ Holography
The study and development of holography began in 1947 by scientist Dennis Gabor. Gabor developed The idea of holograms while working on an electron microscope. However he was not able to actually create one. The first hologram was created in 1967 using the research and theories of various Russian and American Scientists who worked from the basic idea of D. Gabor. From this point on holograms progressed through the years.
Holograms today are generated with lasers and can be viewed under a normal incandescent Light bulb. However so far we do not have the technology to create Holographic videos or movies. As late as the recent American election in November, CNN News claimed that they had “beamed in” a live 3-D holographic video feed of a reporter thousands of miles away. News anchor Wolf Blitzer told his colleague, Jessica Yellin, who was apparently being “beamed in” to talk to him "You're a terrific hologram," as she was shown to be projected in front of him. However, this was not a true 3-D Holographic Image. What was shown on CNN was simply a tomograms, which means only the viewers at home could see it. To create a full 3-D holographic video, our technology is still not good enough. To capture a hologram, the use of a laser and High Definition cameras is needed. At this point in time, to create a Human sized Full 3-D hologram a laser with a diameter of 6 meters would have to be used. Light of this magnitude would simply be blinding to the naked eye. With the development of Light Emitting Diodes (LED’s) we are getting closer to creating a proper holographic image, since they are safer than lasers.
The Pros of Holographic Images
Having true 3-D Holographic video would be simply amazing, since you could enjoy video much better. Imagine putting in a James Bond DVD and being a ble to see a life-sized 3-D Bond in your living room. Also it would be beneficial for long distance communication. A soldier in thousands of miles away could see his the actual size of his new born child with greater detail.
References
- http://inventors.about.com/od/tstartinventions/a/telegraph.htm
- http://search.eb.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/eb/article-9053835
- http://go.galegroup.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/ps/infomark.do?action=interpret&u=ucalgary&source=library&tabID=T001&Z3950=1&userGroupName=ucalgary&docId=CX3401200236&type=retrieve&version=1.0&productId=GVRL&authCount=1
- http://find.galegroup.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/itx/infomark.do?prodId=CPI&userGroupName=ucalgary&version=1.0&type=retrieve&docId=A110361173&searchType=AdvancedSearchForm
- http://www.cbc.ca/technology/story/2008/11/05/tech-holograms.html
- http://www.holography.ru/histeng.htm
- http://www.nalc.org/news/precord/0101-mailmillennia1.html
- http://bnrg.eecs.berkeley.edu/~randy/Courses/CS39C.S97/beginning/beginning.html
- http://inventors.about.com/od/bstartinventors/a/telephone.htm
- http://inventors.about.com/library/weekly/aa070899.htm
- http://searchwarp.com/swa241109.htm
- http://prosandcons.us/?cat=40
- http://www.improve.com/children-and-computers.php
- http://searchunifiedcommunications.techtarget.com/sDefinition/0,,sid186_gci213055,00.html