GROUP 7
Contents
Group Members
Jingwen Ren, Faye Stenning
Initial problem Statement
Google Inc. is an American public corporation, earning revenue from advertising related to its Internet search, e-mail, online mapping, office productivity, social networking, and video sharing services as well as selling advertising-free versions of the same technologies. The Google headquarters, the Googleplex, is located in Mountain View, California. As of 30 September 2008 the company has 20,123 full-time employees. Today, Google is a publicly traded company that handles one of the most used search engines in the world, Almost 60% of the market in search engine usage is controlled by Google, and most analysts Google.It helps people reach information quickly and efficiently. We are going to talk about the history of Google google's function, including its software and other service. We will also introduce that how google works and Ranking-the vital part of search engine.We will introduce google's revenue in the end.
Google Overview
Google is a global technology leader focused on improving the ways people connect with information. Their innovations in web search and advertising have made their web site a top internet destination and their brand one of the most recognized in the world. They maintain the largest, most comprehensive index of web sites and other content, and they make this information freely available to anyone with an internet connection. Their automated search technology helps people obtain nearly instant access to relevant information from our vast online index.
A Brief History of Search Engines
The first tool for searching the web was created by a man named Alan Emtage. The engine, named Archie, was designed in 1990 at McGill University. Shorty after Archie’s release, two new engines emerged, Veronica and Jughead. These three engines could only search through an index of compiled sites. The first engine to search the entire web, based on text searches, was Webcrawler. This tool was developed in 1994 by Matthew Gray, and quickly shaped the standards for future search engines. During the next few years, many different engines took shape and volleyed for market share. Google made its introduction in the late 90’s and quickly became the most popular search engine.
The History of Google
Google first began as a research project by Larry Page at Stanford University in 1996. Shortly after the outset of the research project, Sargey Brin joined the team. The web crawler was launched in March of 1996 and shortly after the two friends quickly began developing a way of organizing and ranking the importance of the information the web crawler was creating. After reviewing the project, it became apparent that this method of ranking information would translate well into a search engine. The name Google was a play on the number googol (1.0 × 10100), twists on mathematical terms would become a characteristic trait of Google. The domain google.com was registered in Sept of 1997, followed by the incorporation of Google Inc a year later. After outgrowing two locations, the company moved into a complex rented from Silicon Graphics Inc (SGI). The Googleplex, also another twist on a mathematical term, was purchased from SGI 7 years later for $319 million.
Functions Of Google
Google is most often used as a search engine; however it has numerous functions apart from being just your basic search engine.
Google Search
Google has categorized specific search requests together making it easier for users to find what they are looking for. Some off these categories include blogs, books, catalogs, finance, images, maps, news, scholars, videos, and even a university search which allows you to search within a specific school website. Another popular search function of Google is Google Earth which uses satellite imagery to allow you to view any place of your choice including galaxies in the sky! Two other search functions of Google include Google Alerts and Desktop Search. Google Alerts are updates of the latest Google results done by e-mail. These updates are based on any topic of your choice. Desktop Search is like a web search but instead of searching the web Google will easily and efficiently search your computer bringing up files and documents.
Google Communication
Some functions relating to the communicating aspect of Google include You Tube, Google Translate, Picasa, Google Talk, Google Docs, and Gmail. You Tube allows you to watch and share videos, Google Translate takes any webpage and translates it into a language of your choice, Picasa allows you to find, share and edit your photos, Google Talk enables you to instant message or call your friends through your computer, Google Docs allows your create and share your online documents, presentations and spreadsheets on line and lastly Gmail is just your basic everyday email.
Google Mobile
Another quality of Google which is growing in popularity is Google Mobile. Google Mobile allows you to use Google searches, maps, Gmail and more right at the convenience of your mobile phone.
These are just a few of the many functions Google has to offer and there are more being created each day.
How Google Works
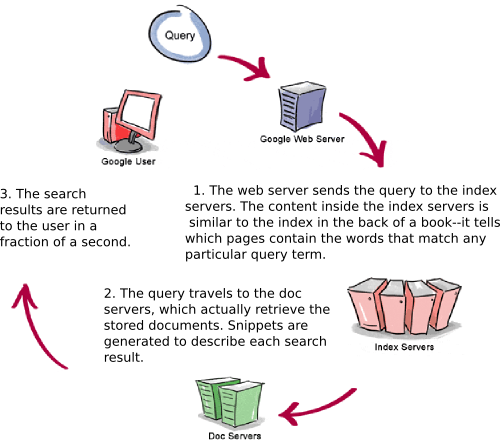
Google runs on a distributed network of thousands of low-cost computers and can therefore carry out fast parallel processing. Parallel processing is a method of computation in which many calculations can be performed simultaneously, significantly speeding up data processing. Google has three distinct parts:
Googlebot a web crawler that finds and fetches web pages
The indexerthat sorts every word on every page and stores the resulting index of words in a huge database
The query processor which compares your search query to the index and recommends the documents that it considers most relevant
Let’s take a closer look at each part.
Googlebot, Google’s Web Crawler
Googlebot is Google’s web crawling robot, which finds and retrieves pages on the web and hands them off to the Google indexer. It’s easy to imagine Googlebot as a little spider scurrying across the strands of cyberspace, but in reality Googlebot doesn’t traverse the web at all. It functions much like your web browser, by sending a request to a web server for a web page, downloading the entire page, then handing it off to Google’s indexer.
Googlebot consists of many computers requesting and fetching pages much more quickly than you can with your web browser. In fact, Googlebot can request thousands of different pages simultaneously. To avoid overwhelming web servers, or crowding out requests from human users, Googlebot deliberately makes requests of each individual web server more slowly than it’s capable of doing.
Googlebot finds pages in two ways: through an add URL form, www.google.com/addurl.html, and through finding links by crawling the web.
Unfortunately, spammers figured out how to create automated bots that bombarded the add URL form with millions of URLs pointing to commercial propaganda. Google rejects those URLs submitted through its Add URL form that it suspects are trying to deceive users by employing tactics such as including hidden text or links on a page, stuffing a page with irrelevant words, cloaking (aka bait and switch), using sneaky redirects, creating doorways, domains, or sub-domains with substantially similar content, sending automated queries to Google, and linking to bad neighbors. So now the Add URL form also has a test: it displays some squiggly letters designed to fool automated “letter-guessers”; it asks you to enter the letters you see — something like an eye-chart test to stop spambots.
When Googlebot fetches a page, it culls all the links appearing on the page and adds them to a queue for subsequent crawling. Googlebot tends to encounter little spam because most web authors link only to what they believe are high-quality pages. By harvesting links from every page it encounters, Googlebot can quickly build a list of links that can cover broad reaches of the web. This technique, known as deep crawling, also allows Googlebot to probe deep within individual sites. Because of their massive scale, deep crawls can reach almost every page in the web. Because the web is vast, this can take some time, so some pages may be crawled only once a month.
Although its function is simple, Googlebot must be programmed to handle several challenges. First, since Googlebot sends out simultaneous requests for thousands of pages, the queue of “visit soon” URLs must be constantly examined and compared with URLs already in Google’s index. Duplicates in the queue must be eliminated to prevent Googlebot from fetching the same page again. Googlebot must determine how often to revisit a page. On the one hand, it’s a waste of resources to re-index an unchanged page. On the other hand, Google wants to re-index changed pages to deliver up-to-date results.
To keep the index current, Google continuously recrawls popular frequently changing web pages at a rate roughly proportional to how often the pages change. Such crawls keep an index current and are known as fresh crawls. Newspaper pages are downloaded daily, pages with stock quotes are downloaded much more frequently. Of course, fresh crawls return fewer pages than the deep crawl. The combination of the two types of crawls allows Google to both make efficient use of its resources and keep its index reasonably current.
Google’s Indexer
Googlebot gives the indexer the full text of the pages it finds. These pages are stored in Google’s index database. This index is sorted alphabetically by search term, with each index entry storing a list of documents in which the term appears and the location within the text where it occurs. This data structure allows rapid access to documents that contain user query terms.
To improve search performance, Google ignores (doesn’t index) common words called stop words (such as the, is, on, or, of, how, why, as well as certain single digits and single letters). Stop words are so common that they do little to narrow a search, and therefore they can safely be discarded. The indexer also ignores some punctuation and multiple spaces, as well as converting all letters to lowercase, to improve Google’s performance.
Google’s Query Processor
The query processor has several parts, including the user interface (search box), the “engine” that evaluates queries and matches them to relevant documents, and the results formatter.
PageRank is Google’s system for ranking web pages. A page with a higher PageRank is deemed more important and is more likely to be listed above a page with a lower PageRank.
Google considers over a hundred factors in computing a PageRank and determining which documents are most relevant to a query, including the popularity of the page, the position and size of the search terms within the page, and the proximity of the search terms to one another on the page. A patent application discusses other factors that Google considers when ranking a page. Visit SEOmoz.org’s report for an interpretation of the concepts and the practical applications contained in Google’s patent application.
Google also applies machine-learning techniques to improve its performance automatically by learning relationships and associations within the stored data. For example, the spelling-correcting system uses such techniques to figure out likely alternative spellings. Google closely guards the formulas it uses to calculate relevance; they’re tweaked to improve quality and performance, and to outwit the latest devious techniques used by spammers.
Indexing the full text of the web allows Google to go beyond simply matching single search terms. Google gives more priority to pages that have search terms near each other and in the same order as the query. Google can also match multi-word phrases and sentences. Since Google indexes HTML code in addition to the text on the page, users can restrict searches on the basis of where query words appear, e.g., in the title, in the URL, in the body, and in links to the page, options offered by Google’s Advanced Search Form and Using Search Operators (Advanced Operators).
Let’s see how Google processes a query.
PageRank
What is PageRank
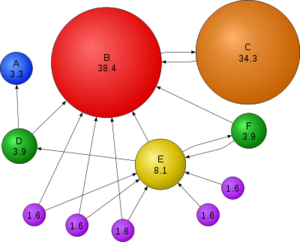
Ranking plays a vital part in the world of Search Engine Optimization. Google's PageRank technology is in fact the very heart of the Google algorithm.In short PageRank is a “vote”, by all the other pages on the Web, about how important a page is. A link to a page counts as a vote of support. If there’s no link there’s no support
How Does it Work
Vote PageRank determines page ranking based on popularity,Google interprets a link from page A to page B as a vote, by page A, for page B. Google looks not only at the sheer volume of votes; among 100 other aspects it also analyzes the page that casts the vote. it can be likened to a giant electronic voting system. Using that terminology, It stands to reason that the page with the most votes
Not all links weight the same PageRank is determined not just by link quantity, but also by link source importance. With PageRank, five or six high-quality links from websites such as www.cnn.com and www.nytimes.com would be valued much more highly than twice as many links from less reputable or established sites.” important weigh more heavily and help to make other pages "important." Using these and other factors, Google provides its views on pages' relative importance." So in order to increase your PageRank, you need to get as many links as possible from other websites into yours, especially sites with the higher PageRanks, as they can have an amazing impact on your rank. For example, just one link from a PR10 page would normally be enough to increase your websites rank to PR8, but to get to that same rank from a PR3 page would probably require somewhere in the region of about 350,000 links.
The way PageRank functions across the entire web is by means of a logarithmic pattern, where there are very few pages with a PR10 (PageRank 10, the highest you can get), but hundreds of thousands with a PR0 (the lowest). In order for the average to stay at 1, any increase in the PR of one page is offset by a very small reduction in the PR of every other page.location of keywords on your web page.It would appear that the higher the particular keyword appears on the page, the higher the ranking, and this applies to your title tag as well. For example, if you had a website that sells laptops, which would be one of your keywords, but you didn't use the word "laptops" in your title tag, then your ranking would be lower than a website that did. This is because keyword placement is a fundamental aspect to search engine optimization and is something that Google's PageRank analyzes.
The frequency of keywords also plays a factor in PageRank. A page about laptops which uses that word 5 or 6 times, may receive a higher ranking than if you used that word only 2 or 3 times.
Google advertising
ADwords Program
One of the absolute best online marketing processes available to any business today is Google's AdWords Select advertising program. AdWords is Google's flagship advertising product and main source of revenue ($16.4 billion in 2007)It costs a mere $5. USD to setup a campaign and requires a credit card submission at startup. Google's Pricing Model Google charges on a CPC ("Cost per Click") basis - pay for each clickthrough to your web site from Google's, no more no less. Keywords costs can vary tremendously ranging from $.05 to $11. USD or more per keyword - Google assigns a "minimum cost per click" for specific keywords based on "market value" and "performance history" via Google's AdWords Select program history. Be prepared to pay a much higher rate for very popular keywords and this is a moving target all of the time - the more popular this program becomes the more you will be forced to pay for selected popular keywords.
How ADWords Program works
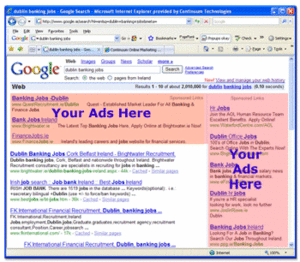
You create your adsYou create ads and choose keywords, which are words or phrases related to your business. Get keyword ideas
Your ads appear on Google When people search on Google using one of your keywords, your ad may appear next to the search results. Now you're advertising to an audience that's already interested in you.
You attract customers People can simply click your ad to make a purchase or learn more about you. You don't even need a webpage to get started - Google will help you create one for free. It's that easy!
Benefits of Pay Per Click Advertising
PPC or CPC paid advertising puts you in front of your target market at the time they are actively seeking your product or service. Unlike traditional advertising such as newspapers, TV, radio, billboards, magazines, etc. Pay Per Click search engine marketing only costs you money when someone actually looks for your service by searching for it in a search engine and clicks on your ad. A Pay Per Click Campaign takes immediate effect bringing potential customers to your website from day one.
Revenue From Advertising
99% of Google's revenue is derived from its advertising program.They generate revenue primarily by delivering relevant, cost-effective online advertising. Businesses use their AdWords program to promote their products and services with targeted advertising. In addition, the thousands of third-party web sites that comprise the Google Network use our AdSense program to deliver relevant ads that generate revenue and enhance the user experience
References
Jingwen Ren
- How Google Finds Your Needle in the Web's Haystack by the American Mathematical Society
- Googles AdWords Select(tm) Groundbreaking Program
- [http://www.ianrogers.net/google-page-rank/ The Google Pagerank Algorithm
and How It Works]
- Financial Tables
- learn about ADword
- pay per ckick advertising
- what do we really know about PageRank
- [1]
- how google works
- GOOGLE ANNOUNCES THIRD QUARTER 2008 RESULTS
Brendon Sauer
- "Corporate Information: Google Milestones." Google. Retrieved on November 23, 2008.
- “The best advice I ever got” (Fortune, April 2008)
- Koller, David. "Origin of the name, "Google." Stanford University. Retrieved on November 23, 2008.
- Olsen, Stefanie. "Google's movin' on up." CNET. Retrieved on November 23, 2008.
- Staff Writer. "Google to buy headquarters building from Silicon Graphics." Silicon Valley / San Jose Business Journal. June 16, 2006. Retrieved on November 23, 2008.
- “Search Engine History” Retrieved on November 23, 2008.
Faye Stenning