Group 4:Brittany Burns - Joyce - Amanda - Stephanie - Ying
Contents
GPS: Global Positioning System
What is GPS?
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a global navigation satellite system that was developed by the United States Department of Defense. It uses between 24 and 32 Medium Earth Orbit satellites that transmit precise microwave signals, which allow GPS receivers to determine their current location, time, and velocity. The U. S. and Allied military, certain U. S. Government agencies, and selected civil users with authorized cryptographic equipment and keys use the Precise Positioning System. This system has 22 meter Horizontal accuracy, 27.7 meter vertical accuracy, and 200 nanosecond time accuracy. Civil users use the Standard Positioning Service. This system has 100 meter horizontal accuracy, 156 meter vertical accuracy, and 340 nanoseconds time accuracy. GPS errors are a combination of noise, bias, blunders. Since 1993 GPS has become a widely used aid to navigation worldwide. It is a useful tool for map-making, land surveying, commerce, and scientific uses.
Privacy IssuesGPS applications can be installed in cell phones, cars and clothing. These uses of GPS raise the issue of whether or not your privacy is being protected, and if it is not, just who can access your information and know your whereabouts. Depending on where you live there are different Privacy Laws in place to protect your information. However, as technology evolves it becomes more and more difficult for privacy laws to adapt and keep up with such fast changed advancements. Technology makes it much harder for you to protect your personal information, and a lot easier for other people to gain access to information that they don’t have authorization to see. In Canada individuals are protected under multiple privacy acts. The Privacy Act protects individuals against infringement by government organizations, and the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act which includes the protection of data privacy. There are many instances where people use GPS to track their children, either through clothing, or cell phones. This aids in the protection of their children at school, or elsewhere, but also infringes the child’s privacy rights. Business’s use GPS in company cars so that they know where employees are, and whether they are where they are supposed to be, and doing what they are supposed to be doing. All of these examples appear to draw a thin line between protection and privacy. Advantages GPS has many advantages even in the case of privacy of your location. It is used for location in life saving missions such as aviation, ground and maritime operations. Many GPS sport clothing has been manufactured to allow easy location of your where abouts in the event of emergency. Another advantage of GPS is that it can determine where you are and how to find your destination. You are also able to track your route and find your way back to your origin. If you do not want to be tracked there is an option to turn off your GPS receiver as well as to turn of the GPS in your cell phone or other devices. More advantages include the ability to find stolen cars at ease now, since GPS receivers provide 3D location (latitude, longitude, altitude, and time). Other areas that are also assisted by GPS are banking, cell phone operations, and power grids, shich use the accurate timing of GPS. Farmers, surveyors, and geologists also use GPS for its percise 3D location. DisadvantagesAlthough GPS has many advantages, there are still some very important disadvantages. First of all in the case of privacy, GPS has the ability to track anyone with a receiver and can trace where you have been. Other disadvantages have technical issues. The GPS signal from the satellites can be delayed from the bouncing off of high buildings, which gives the GPS receiver the impression that the satellite is further away. GPS receivers also don't recognize mountains, rivers, and any obtrusions, therefore giving misleading directions. The signals are also not received inside of most buildings, caves, forests, and heavy clouds. When travelling you should always keep a map and compass on hand for back up because of GPS inaccuracy in the case of road closures, road construction, and new roads. And most of all they run on batteries, therefore they'll probably run out when you need it the most. Other OptionsThere are some other satellite navigation systems besides GPS, which include: the Compass System (from China), the Galileo Global Navigation Satellite System (from the European Union and European Space Agency), the GLONASS (from former Soviet Union and now Russia), the IRNSS (from India), and the QZSS (from Japan).
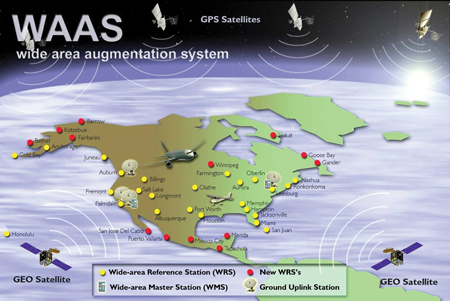
Augmentations
ConclusionThe GPS system can influence one’s life both positively and negatively. It can help guide you to your wanted destination, help you get on track when you are lost, and even help find someone that is missing. It can also be an invasion of a person’s privacy rights and people generally may not want other people to be following their every move. Whether one approves of the system or not, GPS today not only plays a large role in collecting data, but also is being integrated into many people's daily lives. It is now available on many cell phones as well, which are used by many people. By conducting this research on GPS, we support the idea that the GPS system is a major contributor to the technological world of today (Seabourne 2009). ReferencesDas, A. (2007). GPS augmentation system. Location, the portal on positioning and navigation. Retreived April 02, 2009 from http://www.location.net.in/magazine/2007/jan-feb/20.htm. (n.d.)."Compass (BeiDou 2) Satellite Navigation System.” SinoDefence.com. Retrieved March 29,from:http://www.sinodefence.com/space/spacecraft/beidou2.asp (n.d.). “Galileo”. European Commission. Retrieved March 29, 2009, from: http://ec.europa.eu/transport/galileo/index_en.htm. (n.d.). “GLONASS - Summary”. Andrews Space & Technology. Retrieved March 29, 2009, from: http://www.spaceandtech.com/spacedata/constellations/glonass_consum.shtml (n.d.). “Satellite navigation: Galileo”. EUROPA. Retrieved March 29, 2009, from: http://europa.eu/scadplus/leg/en/lvb/l24205.htm Raghu,K. (Sep 5 2007). “India to build a constellation of 7 navigation satellites by 2012”. livemint.com. Retrieved March 29,2009, from : http://www.livemint.com/2007/09/05002237/India-to-build-a-constellation.html Ronca, D. (2009). Which is better for navigation -- compass or GPS?. "HowStuffWorks". Retrieved March 25, 2009 from http://adventure.howstuffworks.com/compass-or-gps5.htm Salada, M. (2007). Pros and Cons of Auto Navigation Systems and GPS Devices. "Associated Content". Retreived March 25, 2009 from http://www.associatedcontent.com/article/142525/pros_and_cons_of_auto_navigation_systems.html. Seabourne, B. (2009). GPS security and privacy – pros vs cons. Ezine articles. Retreived April 02, 2009 from http://ezinearticles.com/?GPS-Security-And-Privacy---Pros-Vs-Cons&id=945696. Terada,K. (Oct. 20, 2008). “L-antenna Sinusoidal Vibration Test”. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. Retrieved March 29, from: http://www.jaxa.jp/projects/sat/qzss/index_e.html |