Talk:Courses/Computer Science/CPSC 203/CPSC 203 Template/CPSC203 Term Projects
Contents
- 1 LIAR, LIAR...PANTS ON FIRE! POLYGRAPHS AND THEIR ABILITY TO DETECT LIES
- 2 Team Information
- 3 Introduction to Technology and Issue
- 4 History of the Polygraph
- 5 What is a Polygraph Machine?
- 6 How is a Polygraph Exam Conducted?
- 7 The Pros of Using a Polygraph Machine
- 8 The Cons of Using a Polygraph Machine
- 9 Did You Know?
- 10 Concluding Argument
- 11 References
LIAR, LIAR...PANTS ON FIRE! POLYGRAPHS AND THEIR ABILITY TO DETECT LIES
Team Information
Team Members
- The Interrogators
- Josh Cheek
- Michael Beckett
- Bjorna Pumo
- Marcene Naidoo
Team Contacts
- Josh Cheek - jtccheek@ucalgary.ca
- Michael Beckett - michaelandrewbeckett@hotmail.com
- Bjorna Pumo - bpumo@ucalgary.ca
- Marcene Naidoo - mnaidoo@ucalgary.ca
Introduction to Technology and Issue
Technology: Polygraph Machines
Issue: The inability of the polygraph to always produce accurate results.
Since the polygraph was first invented, the myth surrounding this machine has been that it is used to determine whether a person is lying or is being honest. Contrary to popular belief, this is not the case. A polygraph can be better described as a machine used to measure a person’s bodily responses. If the individual is capable of altering his or her bodily response during a lie detector test, it will dramatically affect the results of the test. This, combined with the fact that many scientists do not believe that the polygraph has a scientific basis, makes the use of polygraph machines a very controversial topic.
History of the Polygraph
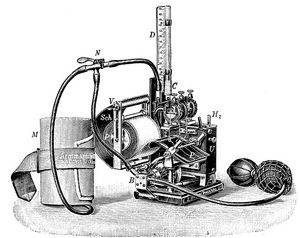
The earliest attempt to invent a machine that would detect lies, was made in 1895 by Italian criminologist Cesare Lombroso. His device named “Lombroso’s Glove”, recorded changes in blood pressure when an individual was being untruthful. At the beginning of World War I, Vittorio Benumbs conducted lie detection experiments with a device that measured the subject’s respiration. During this time, the US Government commissioned a psychologist, Dr. William M. Marston, to produce a method for the questioning of prisoners of war. He began to conduct experiments by using a sphygmomanometer and taking intermittent readings of the blood pressure during the questioning period. In 1921 Dr. John Larson developed what became known as the forerunner of the modern day polygraph. This instrument was the first to record blood pressure, pulse, and respiration. Leonard Keeler then added another feature of measuring changes to the list; the skins resistance to electricity. Keeler is recognized as the father of the modern day polygraph. He combined three important components that are still used today even though they are more enhanced than they once used to be. The three features are: the pneumograph, cardiograph and the galvanic skin response. Some modern machines have added other electronic devices to the polygraph, however the components introduces by Keeler are still contained in the modern polygraph instrument.
What is a Polygraph Machine?
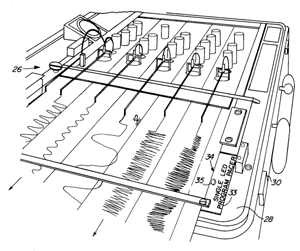
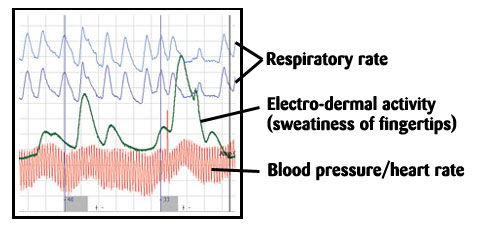
Polygraphy is the science of truth verification based upon psychopysiological analogues. A polygraph polygraph machine then, is an instrument that is used to record changes in one's physiological processes such as heartbeat, blood pressure, respiration and electrical resistance or galvanic skin response or GSR.
There are three types of polygraph tests. The first is a Control Question Test. This paticular test compares the physiological response to relevant questions about the wrongdoing of the subject, with the response to questions relating to possible prior misdeeds. The second test is called a Direct Lie Test. In this instance the purpose is to detect when the subject is not being honest. This by comparing physiological responses when the subject is told to deliberately lie to responses when they tell the truth. The last test, know as the Guilty Knowledge Test is formatted in a manner which allows the subject to answer a multiple choice questions. It then compares physiological responses to these questions. However, in this test one of the choices offered as answers contains information that only the investigators and criminal would know.
How does a Polygraph Machine Work?
A polygraph machine is not a lie detector, but rather an instrument that measures changes in heartbeat, blood pressure and respiration. The underlying theory is that when people become nervous about lying their heart rate will increase. They're also more likely to experience an increase in blood pressure, change in breathing rythms, and increase in perspiration. Any deviation from the baseline of truthfulness is then seen as a sign of lying.
.
How is a Polygraph Exam Conducted?
Conducting A Polygraph Exam: Explanation
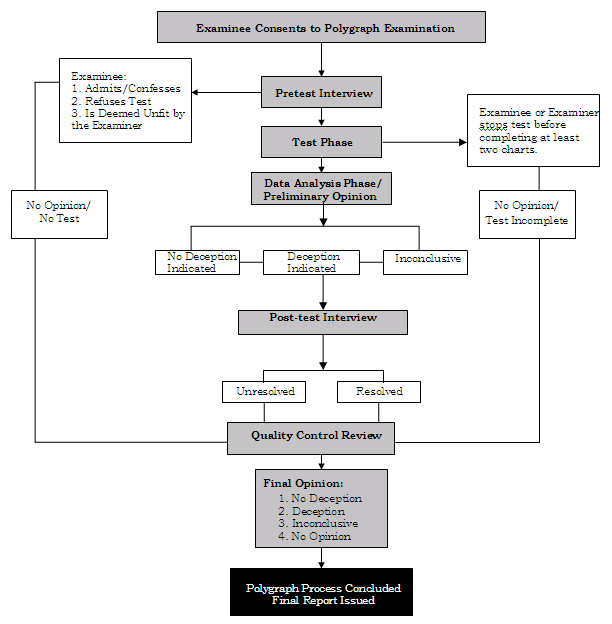
There are a number of steps involved when a polygraph test is conducted. Initially the participant must agree to take the polygraph exam.The next phase is the Pretest Interview. Here the examinee can choose to do one of three things: answer or admit the questions the examiner wishes to test him/her on, change his/her mind about wanting to be examined, or he/she can be deemed unfit to take a polygraph test by the examiner. If the subject wishes to go through with the test, he/she then enters what is called the Test Phase. In this stage of the game, the examiner questions the examinee. Both the examinee and the examiner have the choice to stop the test if they so wish, during the Test Phase. If however neither of the two decides to stop half way through the examination, the test is completed and the examiner obtains the results of the test. He then determines if the examinee has been truthful or not. The results can also be inconclusive, which would likely mean that the subject would have to be tested again. In the Post Test Interview, the examiner makes a decision about whether he has sufficient evidence to produce a final report. After this is done, the examiner does a Quality Control Review, where he forms a final opinion on whether there has been deception indicated in the test, or if the results are inconclusive. Finally, the examiner issues a final report on the questions that the examinee has answered.
The Pros of Using a Polygraph Machine
The public sector has greatly increased its use of the polygraph to help determine “just how loyal their workers are”. The polygraph has been proved especially useful to companies that want to protect classified information. This is especially useful in the case of central intelligent agencies, and commercial companies (such as brand name clothing companies) who want to protect the uniqueness of their products. The pentagon averages over 23 000 polygraph tests every year. Law enforcement agencies have also turned to polygraphs to screen applicants. In this case, the polygraph has proven to be a great way to provide companies with loyal and serious workers.
The Cons of Using a Polygraph Machine
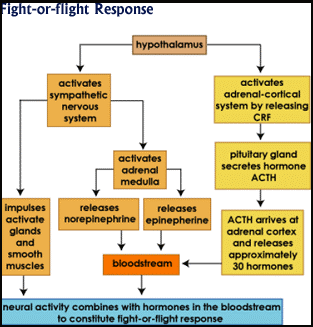
The extent to which a person can control their physical reactions is a huge factor when it comes to lie detector tests. Some people are extremely nervous, while others are unshakable. Since the lie detector measures every movement of the body, all of this is reflected in the results of the polygraph test. The flight of fight response wich is caused by reactions such as ervousness, anger, sadness, embarrassment, and fear can play a part in altering an individuals heart rate, blood pressure, and/or respiration rate. Having to go to the bathroom can also influence the outcome of a test. Moreover, there are a number of medical conditions (ie.colds, headaches, constipation, or neurological and muscular problems) which can be reasons for the physiological changes measures by the polygraph. It has never been proven that an expert can determine with certanty when one's bodily changes are due to a lie, and when they are due to other unrelated factors. Even if the device measures nervousness, one cannot be sure that the cause of the nervousness is fear of being caught in a lie.This makes the polygraph ideal for the “unshakables”, but at the same time puts all nervous wrecks at a great disadvantage, making the polygraph a very unreliable instrument. In addition, the examiner has to accurately interpret the results. This includes examining the person’s body language, as well as the person’s psychological responses. Most of the time the results are analysed by a single person, and there have been reports where in a number of cases the results were in fact interpreted in a wrong manner.Furthermore, the polygraph does not work for all cases. This is especially true when it comes legal matters. Using the polygraph to make life changing decisions could be very risky. The polygraph may be a useful tool, but because it is not 100% accurate, it is dangerous if used in court decisions, where one's life would then be depended on the results of a test.
Did You Know?
Although the polygraph, or “lie detector” device, is widely acknowledged by the general public as a way to decipher the truth from the non truth, many scientists agree that there is little evidence that polygraphs can accurately detect lies. Prominent psychologist Dr. Leonard Saxe affirms that the idea that we can detect a person's veracity by monitoring psychophysiological changes is more myth than reality. Moreover, the scientific basis behind the polygraph test is largely theoretical; there is no evidence that any pattern of physiological reactions is unique to deception. For example, an honest person may be nervous when answering truthfully and a dishonest person may be non-anxious. Sociopaths fit this example of a non-anxious, but potentially guilty test subject. Because a sociopath’s mind is structured differently from non-sociopaths, their minds create justifications for such deviant behavior such as murder, theft; etc which would therefore render the polygraph test useless in determining if a sociopath is lying. The questionable validity of the polygraph, in certain instances, has resulted in wide skepticism and the wide dismissal of the reliability of the polygraph.
Concluding Argument
Although we see polygraph devices incriminating accused murderers and robbers on our favorite Hollywood TV shows and movies, in real life, the polygraph cannot detect deception. Moreover, the lack of empirical evidence reaffirms the questionability of the polygraph as a reliable deception detecting instrument. Due to this lack of solid, scientific evidence, drawing a conclusion from the polygraph test to determine someone’s innocence or guilt does not pay credence to the legal maxim of “beyond a reasonable doubt”, ultimately rendering the polygraph test as a non-reliable and therefore non-valid way to decipher the truth from the non-truth.
Tune in and watch Michael Shermer test the polygraph and it's ability to detect lies:
.
References
1. http://www.usdoj.gov/oig/reports/plus/e0608/intro.htm
2. http://www.galianospolygraphe.com/html/brief_history_of_the_polygraph.html
3. http://www.cartoonstock.com/directory/l/lie_detector_gifts.asp
4. http://policeapplicant.wordpress.com/2008/05/07/the-polygraph-test/
5. http://www.psychologymatters.org/polygraphs.html
6. http://vlp.mpiwg-berlin.mpg.de/vlpimages
8. http://www.southcarolinacriminaldefenseblog.com/2008/06/the_pros_and_cons_of_polygraph.html
9. https://antipolygraph.org/cgi-bin/forums/YaBB.pl?num=1196089273/7
10. http://www.entrepreneur.com/tradejournals/article/82535724.html
12. http://people.howstuffworks.com/lie-detector1.htm
13. http://skepdic.com/polygrap.html
14. http://epic.org/privacy/polygraph/
15. http://www.polygraphexaminer.com/index_files/Page559.htm