Courses/Computer Science/CPSC 203/CPSC 203 2007Fall L04/CPSC 203 2007Fall L04 TermProjects/Wireless Networks: Secure or Unsecure
Contents
Team
Initial Statement
Hotspot is a term introduced to the IT world 5 years ago by Nokia, it is an area which offers Wi-Fi access to the Internet. Ever since the introduction of hotspots to the public, many privacy issues have arised from it. We will explore the security concern to the users of hotspots. The primary goal of this project is to provide the reader with an overview of hotspots with a focus on the negative aspects. The following page provides information gathered from secondary research techniques: relevant websites. The topics discussed include: history of the hotspots, how hotspots work, disadvantages of hotspots, the vulnerability of wireless devices, and how to protect yourself from hackers.
Argument
In today’s society, WiFi hotspots are becoming increasingly popular. Recently, many organizations (cities, larger corporations, businesses) are developing wireless works; this is leading towards the growing problems that deal with social and security issues of Wi-Fi technology. Security issues have had a negative effect towards the growth of WiFi hotspots. How easily hackers can gain access to wireless devices is mind-blowing. Today, anyone can access your wireless device, all they need is a free hacking software from the Internet to access your device through hotspots. Hotspots gave a new meaning to crime. The easy access of personal information has been misused by many new potential hackers. Although the growth of Wi-Fi technology and usage are inevitable, users of hotspots must be informed on ways to protect themselves from these dangerous risks.
Video Link: Dangers of Hotspots (An Ecological example)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XURwBbwUymE&feature=related
About Wi-Fi Hotspots
History
During his work at Advance Micro Devices (AMD) in August of 1993, engineer Brett Stewart begets the idea for Wayport to offer public Internet access. Two years later, after Stewart’s proposal of the Wi-Fi hotspots, Wayport’s predecessor intent in presenting public space wireless Internet access. The idea of ‘hotspots’ has become widely accepted in cities. As a result, hotspots began to grow and expand throughout different nations.Although the term and idea of ‘hotspots’ spread, it didn’t come into existence until the IEEE 802.11 was finalized. In 1997, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)had established the initial standard for wireless LANs, 802.11 standard (Wi-Fi). There are three different standards that are defined under 802.11 standard: 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g. In fact, a fourth standard, 802.11n, is currently under development and is expected to be ratified in October of 2008. Each standard have its own complexity and capability that provides access to public local-area networks.
Wi-Fi provides high-speed internet connection via suitable wireless-equipped mobile computing devices, such as laptops or PDAs. As a result, hotspots began expand ranging from McDonald’s to Starbucks’, schools to universities, restaurants to airports, and it’s still spreading. A Wireless city is becoming a reality as hotspots from different areas are linked together to offer a wide range of wireless network.
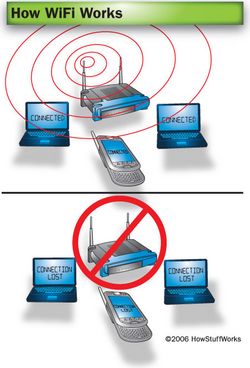
How WiFi Works
Wi-Fi stands for Wireless Fidelity. Instead of using wires to transfer data, wireless internet uses radiowaves for data transfers. A wireless adapter of a computer can translate the data information into a radio signal and transmits the information through an antenna. A wireless router then receives this signal, decodes it, and sends the information to the internet. This process can also work in reverse, in which the router sends the information, and the adapter receives it.
In order to connect to a wifi hotspot, a wireless network adapter is needed. These adapters may already have been built into the computer, otherwise they can be plugged into the PC card slot or USB port. Once the adapter has been installed, it will be able to detect the existing networks and you will have the option to connect to them.
A wireless router is also needed in order to build a successful wireless network. It receives radio signals and provides internet connection.
Disadvantages
A computer’s wireless adapter translates data into a radio signal and transmits it using an antenna. Then, a wireless router is able to receive the signal and decode it. It then sends the information to the Internet using a physical wired Ethernet connection.
One must question whether or not their mobile equipment is secure enough to be used in a hotspot. Before entering a hotspot one must take some precautions to guarantee that they are securely connected to their corporate network or the Internet. Whenever someone uses their mobile equipment in hotspots they must make sure that they have installed firewall software. This is because hotspots are unsecured and people must take responsibility for their own security. When working in a hotspot people must make sure that they are discreet so that others do not view their work. Hotspots are open networks, and therefore are vulnerable to security breaches. This means that one must do whatever they can to protect the data on their PC. If not, this could lead to theft.
Security level
One of the disadvantages of hot spots is the security level. Without proper encryption there is the possibility that somebody would be able to look at personal information that you have on your computer. Wi-Fi networks also have a limited range. The Wi-Fi home router using 802.11 has a range of 45m (150ft) indoors, and 90m (300ft) outdoors. Wireless networks broadcast data over radio waves, and because of this, they can be intercepted (anything that is transmitted over airwaves can be intercepted). This is the main reason why wireless networks are essentially less secure than wired networks. Public wireless networks are designed so that they can be accessed by anyone that is in the Wi-Fi hotspot’s broadcast range (as previously stated about 45m (150ft)). But because these hotspots are open to everyone, it is possible that hackers would be able to snatch your data from the air, decode it, and then use it to their advantage.
Online Banking
In hotspots, when doing your banking online, your transactions are handled carefully over servers that use Secure Sockets Layers (SSL). SSL are an encryption protocol that creates a secure Internet connection. Web retailers that are supporters of SSL direct transactions to an area of a site that is secured by the SSL protocol. These areas of the sites have URLs that begin with https instead of http. There will appear, in the bottom right corner of your browser window, a little lock icon. This is confirmation that the page is secure.
Accessibility to hackers
Wi-Fi is far more realistic than many people might think. In fact, new tools are making it easier than before for hackers to get your account information, without any trouble. The most recent exploit involves the hijacking of web mail and social network accounts. The tools that hackers use work by grabbing the cookies that pass between the “spied-upon” computer and the web page it’s contacting.
Evil Twin
The “evil twin” hotspot is a rising danger for users who rely on public hotspots for Internet access. For the hacker, the trick is simple. The hacker just needs to create a hotspot that has a similar name to that of a legitimate hotspot nearby. The goal of the hacker is to collect user names, passwords, credit card numbers, etc. There is not much one can do in order to prevent this from happening. The security software on laptops won’t help if you connect willingly to one of these hotspots.
An evil twin is homemade wireless hotspot. Their purpose is to gather corporate information without the other person knowing anything is happening at all. It’s easy for someone to create an evil twin. All they need to have is a laptop, wireless card and some software. The attacker positions himself in the area of a legitimate Wi-Fi access point. The computer of the attacker then discovers what name and radio frequency the legitimate access point uses. By gathering this information the attacker is now able to send out his own radio signal using the same name. In the past, evil twins have been known, or have been called, “base station clones” or “honeypots”.
Hacking
Wireless networks are much easier to hack into than wired networks. Because it does not require an actual physical connection, Wi-Fi networks are very vulnerable to hackers. Hacking has become so common that there are many websites and discussion groups on the teaching. Any information stored within a PC over a Wi-Fi network is at potential risk because it may be exposed anytime. Wardriving is a common name used for hacking into wireless networks.
Sniffing Programs
All a potential hacker needs is a "sniffing" program which could be easily downloaded from the internet and detect the key for a secured network, all it takes is time. After cracking the key, the potential hacker is able to view any data transmissions over the Wi-Fi network. With these tools, the hackers will be able to see things such as the websites you're visiting, login information, etc. That is also known as a "channeling" attack on the clueless users who are connected to a hotspot.
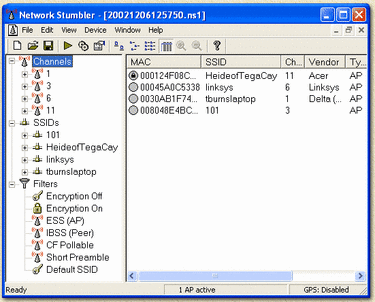
The first step to hack a wireless network is locating one. This is what the "sniffing" softwares are for. A popular software example of this is NetStumbler. This particular tool monitors traffic and airwaves for nearby Wi-Fi networks, gathering data from each one detected, without leaving any trace of intrusion. Kismet is another useful wardriving program; it's not only useful for "sniffing", it's also useful for eavesdropping on the transmissions of data. Kismet can also detect and display wireless networks that are not displaying their SSID (Service Set Identification - public name of a wireless network), which NetStumbler lacks. Tools like these can also be used as a check for your own Wi-Fi security, by using them in attempt to hack into your own computer and test out its security.
Cracking Programs
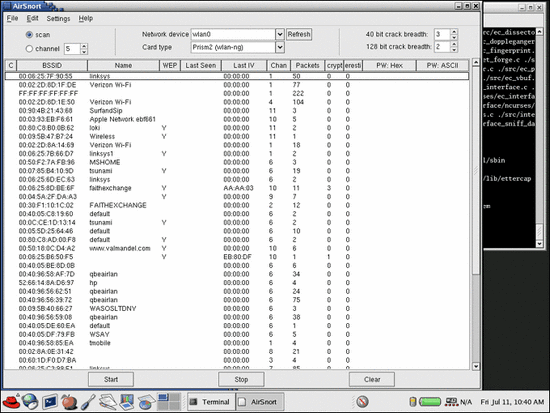
After locating a wireless network, the next step is try to connect to it. If the wireless network you try to connect to does not use an authentication or encryption security, you can simply connect to the SSID. If the network does use some kind of security protection, AirSnort is another software you can download from the internet, for cracking WEP (Wireless Encryption Protocol - encryption technique to secure a wireless connection) Keys. Cowpatty and ASleap are another 2 softwares for cracking WEP keys.
Finally, after you've connected to the wireless network, you can sniff around for data flying through the air at any given moment, but you need to have a program that will help you see these data. Wireshark (formally Ethreal) is able to scan these data flowing around and filters them.
All of the above softwares are available for free downloads on the internet.
Social Concerns
There are many social concerns that come about with wireless internet and hotspots. One of the main social concerns with wireless internet would be privacy. Any information you send over the internet while using wireless internet can be picked up from some one who knows how to hack, this is called side jacking. If you use wireless internet for online banking, shopping or even just e-mail someone can get your bank account information, credit card information and/or any of the personal information you used to sign up for an e-mail account. With this information someone can steel your identity. This means they can pretend to be you when they are purchasing items with your credit card, transferring money out of your bank account, signing up for websites and so on. A well versed hacker can also hack into your computer and delete files or plant new files such as a virus or worms. If they hack into the wifi operation system and plant a virus there the virus could then be sent to all users of the wifi source. Think of the chaos if someone was able to plant a virus in the universities wifi operation system. They could also take files from your computer and post them on the internet. Let’s say you keep a personal diary on your computer, they could take your personal secret diary and send it to all your friends on your e-mail address list. Another basic concern would be wireless internet is not as fast or as reliable as cabled internet. This concern increases with the number of users taping into the wireless internet source. Meaning for many users to use one wireless internet source the source has to be very powerful in order to keep the connection reliable and fast. If you have your own personal wireless router in your home that is not encrypted this can be a major concern because all your neighbors within the range of your router can connect to that signal. It has also been shown that other products that send different wave frequencies such as microwaves, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices and baby monitors can cause interference in the wifi signal making it even slower and even more unreliable.Prevention
There is no simple way from preventing hackers from hacking and stealing you’re personal information and data. There is a set of procedures at your must follow to prevent hacker from acquiring your personal information and data. The following set of procedures is a collaboration that we put together from some of the advice we acquired from the experts in the field security in hotspots.
- The first step would be to make sure the hotspots that you are accessing your internet from is a legitimate access point. Be sure to only use a secure wireless network, one that would ask for authorization before you are permitted to use the network. Be sure never to use the first network that your PC identities, because it might just be the hacker sitting near by you, who is placing a access point to hijack your information.
- Another step would be to make sure that your wireless device has firewall software installed and make sure it is turn on. The firewall is software that stops most hacker from accessing your wireless device through the internet and/or network.
- Make sure that your disable all sharing feature on the wireless device. This is another way the hacker can access you wireless device. By having sharing feature such as file share and printer share, hackers can access your PC through the network.
- Make sure that you make all your folders private. Making the folders private makes it more difficult for hackers to access your files.
- We think that one of the best ways to stop hackers from stealing your personal information is to encrypt your files with sensitive information. By encrypting your file it makes sure that one needs the password to see and modify the document.
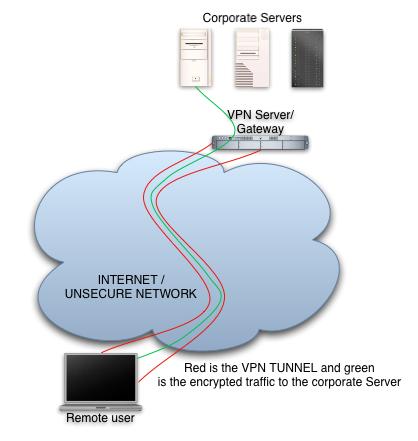
- If possible use a Virtual Private Network or VPN. The software makes sure that your wireless device use tunnel between two access points in a hotspots, your wireless device’s access point and the end point of the hotspots. So VPN makes it very difficult for hacker to access your data.
- Use hotspot locators on search engines:http://www.wi-fihotspotlist.com/
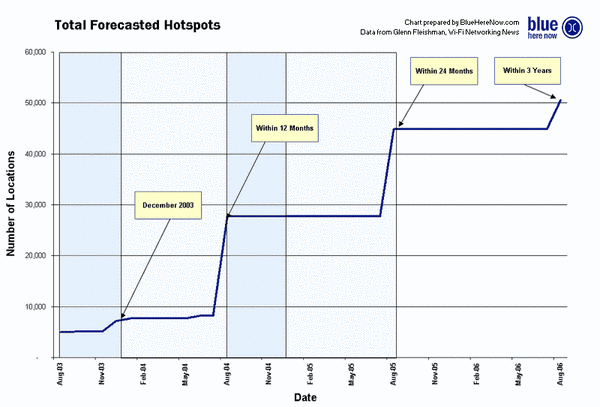
Future of Hotspots
Today’s trend is surfing the web wirelessly with the help of a wireless access point, also known as the Wi-Fi hotspot. The creation of Wi-Fi hotspots allows people to enjoy the freedom by using wireless Internet for free or for a minor charge. Currently, hotspots have been spotted in local fast-food restaurants, coffee shops, schools and universities, and airports. Wi-Fi hotspots do not end there; hotspots are accessible in the great outdoors such as public parks or tourist areas:Video Link: Future of Hotspots
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gmpxmcc_kMQ
At this rate, hotspots will soon dominate over countries and develop the world’s largest wireless network. In other words, wireless networking may become so widespread that you can access the Internet anywhere at any time, without using wires.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi hotspots have become technically advanced areas for communication and research. Because of their convenience and rapidly increasing locales they have become very popular. Their easy access and relatively low costs provide many users with a mobile Internet access. Though they are simple to access there are hidden dangers that many users may not be aware of. This lack of knowledge allows a potential danger to become a reality. Evil twins, lack of proper security software, and hackers are examples of the disadvantages of such technology. The user needs to be aware of the potential for lack of privacy and security while using a Wi-Fi hotspot. Precautions need to be taken in order to secure ones’ information. Wi-Fi hotspots are a rapidly advancing use of technology that has the potential to change the way we access the world.
External Links
1.http://wireless.lifetips.com/faq/103688/0/what-is-a-wireless-access-point/index.html
2. http://search.techrepublic.com.com/search/Wi-Fi+hotspot.html?t=13&s=0&o=0
3. http://courses.aplia.com/problemsetassets/news_analyses/fuller_steal_this_signal/article.html
4. http://www.cnri.reston.va.us/what_is_internet.html
5. http://cfit.ucdavis.edu/internet_futures/event.html
6. http://www.giussani.com/roam/roam_intro.html
11. http://www.myconfinedspace.com
12. http://www.csis-scrs.gc.ca/en/publications/perspectives/200111.asp
13. http://www.oreillynet.com/lpt/a/4081
14. http://www.ethicalhacker.net/content/view/16/24/
15. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wireless_security
17. http://www.districtadministration.com/viewarticle.aspx?articleid=207&p=1#0
18. http://www.wi-fiplanet.com/tutorials/article.php/3623061
19. http://www.microsoft.com/technet/technetmag/issues/2005/1
20. http://www.microsoft.com/atwork/stayconnected/hotspots.mspx
21. http://mobileoffice.about.com/cs/findinghotspots/bb/byusehotspot.htm
22. http://www.allisp.info/wireless/index.html
23. http://www.pcworld.com/article/id,115545/article.html
24. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hotspot_(Wi-Fi)
25. http://computer.howstuffworks.com/wireless-network1.htm
26. http://tech.yahoo.com/blogs/null/23163/beware-the-evil-twin-wi-fi-hotspot
27. http://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/sDefinition/0,,sid14_gci1052455,00.html
28. http://www.wi-fiplanet.com/tutorials/article.php/3623061
29. http://www.geeks.com/techtips/2006/wireless-hotspots-tips.htm
30. http://www.wifinetnews.com/archives/001315.html
31. http://www.serojahotspot.com/home.html
32. http://www.spectrum.ieee.org/archive/1505
33. http://www-rcf.usc.edu/~fbar/Publications/CPR04_BAR_GALPERIN.pdf
35. http://www.wi-fiplanet.com/columns/article.php/3373061
36. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Institute_of_Electrical_and_Electronics_Engineers
37. http://www.selcoms.com/outdoorhotspots.php
38. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.11
39. http://www.wayport.net/Company.aspx
40. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hotspot_%28Wi-Fi%29
41. http://www.microsoft.com/atwork/stayconnected/hotspots.mspx
42. http://www.pcworld.com/article/id,130330/article.html
43. http://www.mttc.org/bts/bts081706.pdf
44. http://www.techsoup.org/learningcenter/connections/page5998.cfm
45. http://www.geeks.com/techtips/2006/wireless-hotspots-tips.htm
46. http://usatoday.jiwire.com/top-wireless-tips-wifi-security.htm
47. http://mobileoffice.about.com/cs/findinghotspots/bb/byusehotspot.htm
48. http://www.ts.vcu.edu/security/lab_compromise.html
50. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wi-Fi
53. http://blog.2blocksaway.com/img
54. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gmpxmcc_kMQ
55. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XURwBbwUymE&feature=related
56. http://hotspot.msn.com/web/SearchView.aspx
57. http://www.wi-fihotspotlist.com/
58. http://computer.howstuffworks.com/wireless-network.htm
59. http://www.sasktel.com/personal/mobility/wifi/index.html
62. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/manitoba/story/2007/09/10/wifi-library.html