Courses/Computer Science/CPSC 203/CPSC 203 2008Winter L03/CPSC 203 2008WinterL03 TermProjects/T19 Group 6 - The Evolution of video games
Contents
Term Project
The Evolution of Video Games and Violence
Team Members
Dan Ehrman, Jordan McLaughlin, Jimmy Hoang
Project Statement
Violence in video games have been an issue for quite some and there is quite a bit of controversy over this topic. A brief history about gaming will be given and video game violence will be discussed and compared to in past video games with more recent ones.
Introduction to the gaming console
The Atari The Original Nintendo The Sega Genisus The Super Nintendo The Nintendo Wii
The Xbox 360 The Playstation 3
History
The first video game was invented in 1952 by A.S. Douglas, it was simply a game of tic tac toe.
- 1958 Tennis For Two
- This is considered to be the first interactive video game ever made.
- 1961 SpaceWar
- Steve Russell wrote Spacewar on a PDP-1, an interactive mini computer which used a cathode-ray tube type display and keyboard input.
First Generation Consoles
- 1972 Magnavox Odyssey
- 1975 Atari: PONG
- 1976 Coleco Telstar
Early Second Generation Consoles
- 1976 Fairchild Channel F
- 1977 Atari 2600 The first ever multi game home video console. The system had plug in cartriges that stored the game information.
- 1978 Magnavox Odyssey 2
Later Second Generation Consoles
- 1982 Atari 5200
- 1982 ColecoVision
- 1982 Vectrex
- 1983 SG-1000
Third Generation Consoles
- 1985 NES
- 1985 Sega Master System
- 1986 Atari 7800
Fourth Generation Consoles
- 1989 TurboGrafx 16
- 1989 Sega Genesis
- 1990 Neo-Geo
- 1991 SNES
Fifth Generation Consoles
- 1993 3DO
- 1993 Atari Jaguar
- 1994 Sega Saturn
- 1995 Sony PlayStation
- 1996 Nintendo 64
Sixth Generation Consoles
- 1999 Sega Dreamcast
- 2000 Sony Playstation 2
- 2001 Nintendo GameCube
- 2002 Microsoft Xbox
Seventh Generation Consoles
- 2005 Microsoft Xbox 360
- 2006 Nintendo Wii
- 2006 Sony Playstation 3
Atari, Nintendo, Super Nintendo, Sega genisus



Violence
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SMQfBvFKaVw
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dFMk17nDUVM&feature=related
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1ExNxpob-_A&feature=related
As stated above, there have been a lot of controversy about the affects that violence in video games have on adolescents. There is a lot of theory and evidence suggesting that medias, such as video games, have a great deal of influence on adolescents.
Some people would argue that since there is a lot of violent content in today's video games it will have a negative affect on children. There is, in fact, evidence that supports this theory. There is a lot of research that have been done in this field of topic, and most of them have resulted in the same conclusion: acute (short-term) exposure and chronic (long-term) exposure to violent video games lead to an increase in aggression and desensitization to "real-world" violence.
Playing violent games is more powerful than simply just watching violence. This is because video games require a certain level of active participation, so when one is playing the game, that person is engaging as the character. The child acts as the character, therefore identifies with this character and is more likely to imitate these actions. Also, video games are based on a reward system. In violent games a player might be rewarded for killing people or destroying something; researchers suggest that constantly engaging in such a system reinforces effective learning.
One study that has been conducted involved two groups, the control group and the experimental group. The control group was given a non-violent game to play for 20 minutes. The experimental group was given a violent game instead. Each participant then competed with another child in a different task and the winner of this task had the opportunity to punish the loser. This punishment consisted of a blast of noise given to the loser. The winner decided how loud it would be on a scale of 1 to 10. The players were told that a blast of a level of 8 or more would cause permanent damage, fortunately, the competitor was imaginary (for safety reasons of course). The results of this experiment showed that the kids in the experimental group (group playing violent video games) sometimes delivered a loud enough noise to make the "competitor" deaf. This study suggests that the result of playing violent games might not always be expressed in a criminal way, but it can be expressed in more subtle ways as shown in this experiment.
Another study looked at the child's brain. This study was set up much like the one previously mentioned. The results of this study shows that the experiment group, which played violent games, had different brain activity patterns: more activity in the region of the brain associated with strong emotions; less activity in the region associated with planning, focus and self-control.
A survey was done on 2032 children ages 8 to 18. It was concluded that, on average, children in grade 3 to 12 play games about 68 minutes a day (including PC, console and handheld); boys, playing games about 6 to 7 days per week, are heavier players than girls are, who play about 1 day per week. It was found that for children ages 12 to 14, 68% of the boys and 29% of the girls had played at least one M-rated (17 years of age or older) game because of the violent and sexual content. Also, it was found that playing these violent video games increased physiological arousal, i.e. blood pressure, heart rate, and sometimes adrenaline and testosterone, etc (these physiological responses are similar to when someone is, for example, in a fight). It was also concluded that violent games had a greater affect on children that are naturally aggressive and hostile and that these children show a higher level in adrenaline and testosterone when playing violent games.
There is, on the other hand, some who would argue that the idea of violent video games increasing aggressive behavior is just nonsense. Looking at the survey mentioned above, a majority of the boys and nearly half of the girls said that they play violent games to relax, 45% of boys and 29% of girls said that these games let them get their anger out and 25% of boys and 11% of girls said they played these games to cope with their anger. Thus, it could be argued that playing violent video games could act as kind of safe outlet for aggression and anger, which would be much better than acting out physically, obviously.
Video games have become more violent over the years. If you look at games like Super Mario Bros, which was released in 1985, there was virtually no violence at all in the game, other than jumping on mushrooms or throwing little orange fireballs. The "violence", if it can even be called that, was incredibly minimal, obviously comical and fictional. But now, violence is even more common in video games, and more intense and extreme as well. Part of the reason that video games have become more violent, I believe, is because of the immense advancement in computer technology and its capabilities of creating very realistic graphics, and the increasingly smaller limitations on what can be done in a game. There are games such as Call of Duty, Rainbow Six, Gears of War, and Grand Theft Auto where the situations of the game can be thought of as very realistic (some more than others), such as the warfare in Call of Duty and Rainbow Six where you/your character are going around killing people and using life-like weapons. In games like Grand Theft Auto, the limitations as to what you can do as a character are very minimal; you can steal cars and crash them into other cars or run someone over, you buy weapons and kill people. The graphics in these games are very realistic. Aggressive_teen_brain.jpg
If video games keep continuing this path, the violence will just continue to get worse and worse. Maybe in the next generation of gaming/gaming consoles the simulations will be so realistic and life-like that players will honestly feel like they really are the character and that they are the ones physically acting out these violent actions.
Present
Xbox 360, PS3, Nintendo Wii
Future
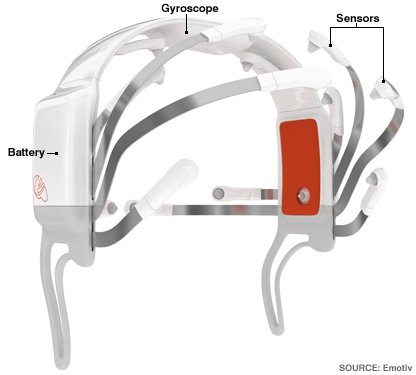
Games Controlled by the mind http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4yqVChaRBsQ&feature=related
The future of the video game industry is heading in the direction of virtual reality. Gamers will soon be able to interact with the virtual world usig their thoughts and emotions alone. A neuro-headset wich interprets the interactons of neurons in the brain is said to be going on the market sometime in the next few years. This new gameing technology is one that has been used in medical practices for almost 100 years but only now has been revolutionized so that is no longer requires a large net of electrodes or a technision to callobrate and oporate it. the headset implements a technology called non-invasive electroencephalography (EEG) which picks up electrical activity from the brain and sends wireless signals to a computer, causing movements and even emotions to apear on your screen as if you were actually doing it yourself. From the video clip above you can see this technology in action, with the headset on you will have the ability to experience a completee intraction with the game as if you were actualy there. The real question comes when the games get to viollent, fighting in actualy wars like in games like Call of Duty and Ghost Recon. What will happen when people actualy gain real war experience through the world of virtual reality. Will our problem with violence become that much worse, its hard to tell right now and there is no real way to forsee the outcome. Eventually this will be an issue to deal with and a very controversial one at that.
References
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_game, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_video_games http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_game_genres http://www.historicaltextarchive.com/s/video-games.php http://culturalpolicy.uchicago.edu/conf2001/papers/walsh.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_game_controversy http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/16099971/ http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2005/03/04/60minutes/main678261.shtml==