Fall 08 - T05 - G1
Contents
Group Information
Contributors
- Usman Afzal
- Matthew Catley (matt246810@hotmail.com)
- Nicholas Chown (rowcanada@msn.com)
- Ryan Cook (The_Architect_RWC@hotmail.com)
- Nathanael Darrell (natster31@hotmail.com)
Technology and Problem
Technology: The Social Web is a technology which affects how individuals socially interact online. It is mostly focused on personal identities, group interactions, creating online reputations, and sharing information. This information can take on many different forms and can include videos, pictures, text, etc. The Social Web includes both video sharing and networking websites. Essentially, any website which has a "socialization" component to it is categorized under the "social web". It allows individuals across the world to communicate and share information.
Problem: Currently, the Social Web seems to be flooded with security and privacy holes which affect more people than ever before. These issues range from small private cases to massive corporate security breaches.
Introduction
Socialization has rapidly changed overtime, and individuals are constatnly being confronted with issues of privacy. In some cases, many are misinformed about the issues of security over the Internet. There are many popular wibsites which can be categorized under the "social web". In this study the most important and influential include Facebook, MySpace, YouTube, and Veoh.
Definition of Security
In this study, our group uses the words security to include individual, group, and business related instances.
This includes:
- Personal Security: The privacy of an individual.
- Educational Security: The security of a group of students.
- Employment Security: The security of individual employees (both potential and hired).
- Corporate Security: The collective and legal security of corporations and their content.
Argument
Due to the increased ability to access information across the Web, easy exploitation of websites, and a lack of education or concern about security, many get negatively exposed. These popular social networking websites are free to millions of individuals. However, for some people these websites have been the most costly sites they have ever used. People need to re-think the value of privacy and really understand how much security is worth on the Social Web in the long run.
Recently, there has been a surge of debate involving the issue of security and privacy on Facebook.
Educational Security
Security does not just involve pictures and videos, it also involves what and how others share written information over the Internet. In the controversial case involving Ryerson University, Chris Avenir, a student studying computer engineering at the university was charged with academic misconduct because information was being shared about course material in a Facebook group. The group was used for academic purposes, students would ask questions, recieve answers, and post comments about homework. Eventually, a professor found out about this and decided to report it. Anyone of the students who was in the study group could have been exposed and accused. However, because Avenir was the group leader the university decided to use him as an example and punish him instead. Avenir had his grade changed from a B to an F in his chemistry course. Eventually, he was expelled. When information can be accessed by anyone, there is an increased risk of consequences. When posting information on social websites like Facebook, individuals should be aware that the security of their information gets reduced and therefore becomes public.
Students should make their profiles private, otherwise any third party or private individual across the world can access it. For instance, two MIT students wanted to show how easy it was to access information on Facebook and so they downloaded around 70,000 profiles of different students from four other universities. They did not do this manually, instead they generated an algorithmic script that automatically downloaded all the profiles. This just shows how easily any third party can collect information about students if their profiles are public.
Employee Security
Today, employers can look at potential employee's Facebook profiles and see what kind of person they are may be hiring. Pictures of individuals doing embarrassing things, videos of illegal activity, or rude comments are common things which employers look for on websites like Facebook.
After a recent study done by the Ponemon Institute and the University of Tennessee, somewhere between 25-43% of employers use Facebook and other social networking sites to screen job applicant, and about 30% of the time it helped determine their decision. The Chief HR Officer of Delta Emerson of Ryan and Company, which is the United States largest independent state and local tax firm stated, “When an individual gets to that point where they're looking for a position they need to realize that facebook becomes an extension of your resume”. There however is a downside to this screen in the employers favor. “You will have access to information on somebody's webpage that is very personal things like religion, sexual orientation, a medical condition. If you do not hire that person, they can come and say that you didn't hire them because of those reasons.” says attorney, Clint David, which could in turn lead to a costly lawsuit.
Several “Farm Boy” (a chain of grocery stores in Ottawa) employees were fired from their jobs for a group they had made on facebook, which they had been openly expressing what they thought about their employers and other employees.
Several employees of the Charlotte-Mecklenburg school board were punished, and one was fired, for offensive comments made on facebook. One teacher was suspended for stating “I hate my student.” on a Facebook group. The school systems Chief Operating Officer sent out a memo to more than 19 000 employees, stating that posting on social networking sites could cost them their jobs.
Personal Security
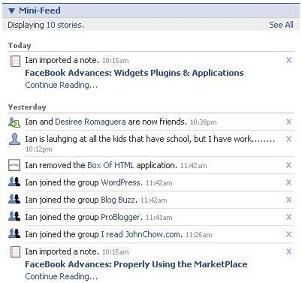
The controversial Facebook "Mini-Feed" is good example related to personal privacy. The Mini-Feed publishes everything you do on Facebook, and anyone who has access to your profile can see this information. So for instance, if someone ended a long personal relationship with another person, everyone would be notified of this as soon as that person changed their profile status - it is obvious that this must be changed.
In September of 2008, the Facebook homepage united the "Wall" and "News Feed" together. Many people disliked this and found that it exposed more individual actions and personal information.
Some components of Facebook which can harm personal security can include:
- Networks - Where do you live or go to school?
- Mini-Feed – Actions you are doing on the site.
- Information/Contact - Anything from phone number, cell number, website, etc.
- Education/Work – Current and past places of work/school.
- The Wall – Viewable conversations with friends/family.
- Friends – Who? How do you know them?
Just in April of this year, Blockbuster was sued for participating in a new beacon advertising program, which broadcasts information about members activity to their friends, via a third part site. This information also pops up on a persons mini-feed. Apparently the members have to option of opt out of this program, but are automatically entered into it. Cathryn Elaine Harris claims that Blockbuster was in direct conflict with the video tape protection program, because this program allowed for people to view the video rental history of other members. Blockbuster claims however, that an adequate amount of privacy protection is in place, and that they are going to fight this case "vigorously".
YouTube
There are video clips of movies, full TV shows, and much more being posted on video sharing websites like YouTube. This represents a breach in the security of the group or business which produced the content. Most video clips, movie trailers, TV shows and other types of videos usually are copyright protected by the particular business which produced it. However without the knowledge or consent of these businesses, most of these videos are uploaded and downloaded numerous times without paying attention to the fact that they are copyright-protected.
Corporate Security
YouTube is the world’s most popular video website. It is a free online site that allows anyone to upload and download video footage, post comments, create and customize status - it is a whole community in itself. Back in 2006, a popular lawyer Robert Tur, who became famous with his detailed aerial helicopter coverage of the Los Angeles 1992 riots and the O.J. Simpson freeway chase in 1994, filed a lawsuit claiming that YouTube posted and circulated videos of his footage without his lawful consent. YouTube, based in San Mateo, said the lawsuit was filed without any specific merit. However, Robert Tur's video clips were removed from the site as soon as they learned of his complaint.
YouTube has not been accused of infringing copyrights just once. Viacom, a leader in the entertainment industry that owns Paramount Pictures, DreamWorks and a variety of cable channels, declared that YouTube infringed its video copyrights more than once and therefore demanded more than one billion dollars in damages. Viacom professed than YouTube crossed the copyright laws by showing more than 160,000 videos without the permission of the entertainment giant which had been viewed an estimated 1.5 billion times by different viewers. YouTube which is owned by Google, however said that it would not draw back, declaring that the law was on its side and that it would fight the court battle. Google, which purchased YouTube not long ago knew that one day it would face copyright challenges and has reportedly set aside large sums of money to fight legal costs. The battle of YouTube with infiltrating corporate security is a long and lengthy one which will only get worse with the amount of lawsuit claims going against it.
Veoh
Corporate Security
Veoh is also another popular video sharing site in which viewers can watch various types of videos. Veoh, just like YouTube has been a victim of lawsuits involving copyright infringement. Veoh has been attacked by Time Warner and Disney for violating copyright laws many times. Just one week after its debut, Veoh was to host a variety of TV shows and other full length programs. This decision was backed by the CEO of Veoh Networks. Despite these announcements by the CEO, Universal Music, the world’s largest music company, claimed that Veoh violated its content - depriving artists and company of revenue and royalties. This led them to sue Veoh, alleging that it was a “massive” copyright infringement claiming millions in damages.
MySpace
Personal Security
One of the largest security breaches in the history of Myspace has occurred just recently. Someone created a script which allowed a hacker to automatically download 17 gigabytes worth of private pictures from the website. He did this by using an automated script on the unstable Myspace website code. The pictures included individuals who were below the age of 16. The whole file was spread around numerous torrent websites. Many vouyers and pedifiles have access to this information - as well as anyone else who has an Internet connection.
Corporate Security
Other social networking sites such as Imeem Inc. and MySpace have also been accused of violating corporate content through piracy. Imeem Inc. (a popular music-based social networking site) was accused of breaching the copyright laws of popular artists such as Madonna, Green Day and the Red Hot Chili Peppers. Warner claimed around $150,000.00 in copyright damages from Imeem Inc. for breaching its corporate security in terms of copyrighted content. MySpace was also accused for not paying royalties and for also playing its role as being a copyright infringer.
Solutions
Public education is perhaps one of the most important ways to help curb security and privacy issues associated with the Social Web. Users of such websites need to be aware of the inherit dangers of putting up personal information. Informing the public how easy it is for hackers and third party groups to gain the information you put on the web is an important step in awareness. When people know the risks, they will be more careful as to what they upload and make accessible to the public. Knowing the extent of freedom that social websites have with releasing users' information also will get the public to speak out to the companies, pushing them to change their security and privacy features. Another way that education helps is in increasing the users' knowledge of the site's own privacy features. When users know the options they have for their own profiles, they are more likely to use them in effective ways.
A second solution to security issues would be for the social websites to hire more monitoring staff/employees. If there are staff designated to the prevention and correction of security breaches, there would be a decrease in such incidences. The number of profiles, videos, and accounts that are created or uploaded daily on each of these sites are so large that this solution might be an unreasonably costly one. A more preventative measure would be to require users to provide some sort of verification when they register. This would help with identity theft by making it harder for people to create fake accounts.
Combating corporate security can also be a difficult and tedious job. However, today it has become a priority to protect copyright material for the prevention of piracy. One such example is video or digital fingerprinting. The electronics company, Philips, has engineered a system capable of identifying copyright-protected material by comparing "digital fingerprints". With a massively widespread database of fingerprint data for secure content, Philips can recognize potential infringement using short video clips and fragments, ranging up to clips of only five seconds in length. Philips plans to make this technology commercially accessible to companies like YouTube as well as other social networking or video sharing websites. Although the system could potentially reduce occurrences of copyright infringement and assist sites like YouTube keep the original content creation business off its trail, there are still some restrictions. Philips Content Identification unit CEO Ronald Maandonks admits that modifications can make the matching process difficult and slow. According to him, the simple process can come across hurdles if the content has been altered due to video scaling, converted to another format or been cropped.
Media Defender, an infamous anti-piracy gang working for the MPAA, RIAA and several independent media production companies, just launched an upload service which they created themselves called “miivi.com”. The main intention of the site is to entrap people into uploading copyrighted material, and then bust and take action against them for doing so. Media Defender is questionable for its crooked actions in the past. Apart from launching video upload services, they also trap people into downloading fake torrents so they can collect IP addresses, and then pass on the information to the Internet Providers. They are trying to achieve the same thing now with their fake download service.
Also YouTube plans to launch anti-piracy software on its website which will assist media companies and recognize pirated videos uploaded by users. However, this possible approach is not getting a warm welcome from users and others in the media industry.
Conclusion
People should act with caution when using the Social Web and any other social networking or video sharing website. There are clearly defined issues of security and privacy related to the fields of personal, educational, employment, and corporate significance. These are all equally important and affect a lot of the world today. With the rise of Web 2.0 and an increasing popularity of social networking sites, the public needs to be more aware the impact of sharing information due to unstable websites, and the increasing amount of access to information.
Ultimately, these free social networking and video sharing websites can really be the most expensive long-term websites people will ever use because of the potential security and privacy issues that come bundled with the Social Web.
References
Ryan Cook
- Ryerson student fighting cheating charges for Facebook study group
- Employers Look At Facebook Too
- Sophos: Bono’s party photos exposed by Facebook privacy issue
- Schneier on Security
- Facebook security glitch exposes user in-boxes
- Perspective: Will security become Facebook's Achilles' heel?
- Facebook security means common sense]
- Student faces Facebook consequences
- Security lapse exposes Facebook photos
- Does what happens in the Facebook stay in the Facebook?
- Facebook's Makeover
- MySpace Bug Leaks 'Private' Teen Photos to Voyeurs
- Fluency, Chapter 13
Usman Afzal
- Lawyer accuses YouTube of copyright infringement
- Viacom sues YouTube for more than $1 billion for infringing copyrights
- Google recognizes infringement threats
- Google’s YouTube will defend against Viacom
- Veoh Networks: A new copyright battlefield
- Veoh sued by Universal Music for massive copyright infringement
- Warner Music sues social network site for piracy
- MySpace meets copyright cops
- Combating copyright infringement with video fingerprinting
- Video fingerprinting vs copyright infringement
- YouTube anti-piracy software policy draws fire
- Anti-piracy gang launches trap to stop piracy
Nathanael Darrell
- Workers fired over Internet postings
- NC school employee fired over Facebook posting
- Employers Use MySpace, Facebook to Screen Applicants
- Facebook & MySpace used by employers as screening device
- Blockbuster sued over role in Facebook's Beacon ad program
- Facebook responds to MoveOn criticism of ad program
Matt Catley
- YouTube - The Complete Profile
- About Facebook
- Facebook Safety
- Copyright And Moral Rights In Works
- YouTube Privacy
- YouTube Statistics - Phenomena
- Internet video search site statistics show YouTube in the lead
- Google Privacy Center
- Intellectual Property Sharing
- Inappropriate Content: Privacy Complaint Guidelines
Nicholas Chown
- Identity Theft
- Add your references here!