T16 Group 3: Andrea, Alex, Naomi, Tyler, Yan
Contents
- 1 T16_Group 3: Andrea, Alex, Naomi, Tyler, Yan
- 2 BitTorrent and its Implications
- 3 What is BitTorrent?
- 4 Bram Cohen
- 5 How BitTorrent Works
- 6 General Terms and Definitions
- 7 Changes in Media Distribution
- 8 Positives of BitTorrent
- 9 Negatives of BitTorrent
- 10 Legal Issues
- 11 BitTorrent Statistics
- 12 BitTorrent Clients
- 13 Best BitTorrent Sites
- 14 Conclusion
- 15 Resources
T16_Group 3: Andrea, Alex, Naomi, Tyler, Yan
BitTorrent and its Implications
Group members: Andrea Moniz, Alex Khunkhun, Naomi Cheng, Tyler Ferguson, Yan Wang
What is BitTorrent?
BitTorrent, developed by Bram Cohen, uses a peer-to-peer connection for the transfer of very large files in a relatively short period of time. BitTorrent has quickly become one of the most common methods among computer users for downloading large files.
A file provider makes their file (or group of files) available to the network by running the BitTorrent protocol. This is called a seed and allows others, named peers, to connect and download the file. When a peer downloads part of the file onto their computer then that part becomes available to the network for others to download. Additional seeds for the file are created when the entire file is downloaded; the peer computer saves the file and if BitTorrent is allowed to run then that computer now becomes a seed computer.
Unlike some other peer-to-peer downloading methods, BitTorrent is a protocol that offloads some of the file tracking work to a central server (called a tracker). Another difference is that it uses a principal called tit-for-tat. This means that in order to receive files, you have to give them. This solves the problem of leeching -- one of developer Bram Cohen's primary goals. With BitTorrent, the more files you share with others, the faster your downloads are. Finally, to make better use of available Internet bandwidth (the pipeline for data transmission), BitTorrent downloads different pieces of the file you want simultaneously from multiple computers.
Bram Cohen
Bram Cohen, is the computer "genius" and chief scientist behind the invention of BitTorrent
Born in 1975, this 34 year old resides in the San Francisco Bay area, CA.
Bram Cohen keeps a publicly accessable blog and resume where many of his interests, hobbies and works are posted.
Bram describes himself as a "Practitioner of evolutionary design and a sworn enemy of waterfall methodology." He is fluent in Python and Java.
Interesting fact: Bram Cohen opts to type using the Dvorak Simplified Keyboard as opposed to the popular QWERTY keyboard.
How BitTorrent Works
The peer-to-peer process:
1) You open a Web page, find the desired file, and start the download by clicking on the provided link.
2) BitTorrent will communicate with the designated tracker in order to gind computer on the network that have the file you requested. Peers that are in the process of downloading the file are also available to draw information from.
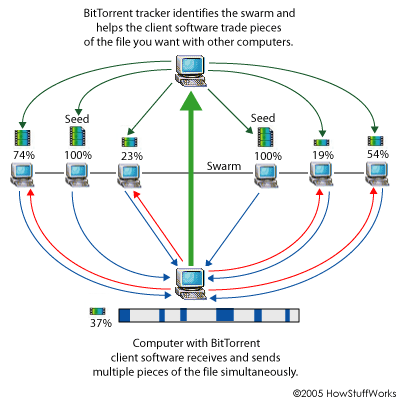
3) A swarm (diagram below) is the network of connected computer that have the file and also computers that are downloading the file. The tracker identifies the swarms and connects your computer to it.
4) The computers within the swarm communicate and trade pieces of the file that they need. The tracker is what identifies what pieces your computer needs. Your computer is able to download several pieces of the file simultaneously from different computers.
5) Once your computer has finished downloading the file you can continue to run BitTorrent in order to allow other computers in the network to download portions of it from you. This improves your download ranking on the "tit-for-tat" system and helps to eliminate the problem of leeching experienced by many other downloading protocols.
Once your computer has finished downloading the file you can continue to run BitTorrent in order to allow other computers in the network to download portions of it from you. This improves your download ranking on the "tit-for-tat" system and helps to eliminate the problem of leeching experienced by many other downloading protocols.
General Terms and Definitions
Client: A program that facilitates the p2p file sharing
Leecher: A user with a very poor share ratio; usually one who only downloads and does not upload.
Peer: A person who has an incomplete file and is downloading.
Seeder: A user that has the completed copy of the file requested and is dedicated to uploading.
Share Ratio: The amount a user uploads over the amount downloaded.
Swarm: A group of users sharing a file using the BitTorrent protocol.
Torrent: A small metadata file that contains the information needed to download the file requested.
Tracker: A server that directs traffic.
Changes in Media Distribution
The MPAA (Motion Picture Association of America) claims to have lost $3.4 billion dollars due to illegal downloading and piracy. The growing availability of television programs, music and films online is threatening the entertainment industry.
What are large companies doing to prevent this loss? Many television stations are beginning to launch on-demand services to combat the damage that Bit Torrent has done. For example, in 2007 BBC launched an on-demand service known as the iPlayer, this gives viewers the ability to purchase a television show for a small fee and view it for up to 30 days. The iPlayer is not just limited to the internet and can be accessed through cellular phones and smart phones. Viewers have a choice of what they want to watch and when they watch it, making this method very convenient. One of the largest groups affected by the illegal downloading and piracy was the Hong Kong film industry. In 1997 Hong Kong films generated around $700 million (in HK currency) by 2004 that number had dropped to $380 million (in HK currency).
Bit Torrent has agreed with the MPAA to stop internet piracy and agreed to remove all links directing users to pirated content. Many new opportunities have opened up through Bit Torrent, for example the video game industry is collaborating with the founder of Bit Torrent, which allows video games to be released through Bit Torrent. Larger companies can also benefit from this because Bit Torrent does give companies the ability to open up a much larger consumer base, thus, increasing business.
Positives of BitTorrent
BitTorrent is generally very efficient as well as effective. The reason for its efficiency is because all downloaders automatically share parts of the file they have, and so clients receive many bits and pieces of the file in a very short amount of time. In addition, BitTorrent encourages altruism; if everyone seeded, downloads would finish even more rapidly, which is what all downloaders are looking for.
The majority of users that use BitTorrent employ it because it is free. Users can obtain music, television show episodes, movies, etc. for no cost at all. By conventional means of acquiring these files, there is some sort of cost associated with it.
Many people believe that all downloadable material via BitTorrent is illegal, but that is far from true. In 2008, CBC became the first major broadcaster to release a primetime television show using BitTorrent technology for users to download, free of charge. In addition, music artists are increasingly using torrents to release demos and other material to pique interest. Through BitTorrent, people have access to music and media they might not otherwise have acquired as they might not have what they want in the area they live in.
There is also the "try before you buy" argument. People may download a song or two by an artist and decide they really enjoy that artist's music, and so they may go out to a traditional store and buy the CD.
Negatives of BitTorrent
BitTorrent opens up the user’s IP address to the public, which makes it easier to track down and may display vulnerability to spywares and Trojan horses. Viruses and Trojans can attach themselves on to all sorts of files such as pictures, videos, and applications. Once the file is opened, the user’s PC will be infected.
BitTorrent also drains incentive from artists and producers to produce more products. In the movie and the music industry this is called discouraged artists. BitTorrent drains incentives because as more products are transferred through file share, bypassing copyrights, artists and producers are making less money thus making the artists and producers unwilling to produce songs/movies/various services they offer. This issue also affects new artists and producers, therefore potential talents may also be discouraged due to lack of incentive of their product as it gets stolen without giving the artists and producers credit.
In an effort to prevent this, many industries and companies are spending huge amounts of money trying to prevent their product from being file shared. However, this creates a vicious cycle: in order to preserve copyright due to file sharing, more money has to be spent either through legal persecution or prevention of file copying, which causes the price of products(movies, music, software, etc.) to go up, which in turn drives more people to file share and obtain the product for free, which create more awareness for the company to prevent file sharing and in turn costs more for the industries… etc. This cycle spirals up.
The last and probably the most critical issue revolving around BitTorrent is the copyright issue. This issue is very controversial because it is between who should be held responsible: the consumers or the service providers. Just as an example, an estimate of 3 billion revenue is lost to non-internet movie piracy annually, and an extra estimate of 1 billion is lost to foreign /oversea movie piracy annually. Not only do this issue concern revenue losses, but it also concerns economic losses as well. Possible economic losses are: income tax loss, unemployment increase and consumption tax losses. As an example, for the music industry last year, economic losses totaled 12.5 billion, seventy thousand job loss totaling 2.7 billion loss in worker’s earning, and almost 1 billion losses on various taxes. The copyright issue also ties back to the discouraged companies and the vicious cycle issue mentioned in the previous two paragraphs. The next section will talk about the legal rights revolving around copyright in more detail.
Legal Issues
In the past few years bittorrent sites have come under attack from government agencies such as the Motion Picture Association of America (MPAA) and the Canadian Recording Industry Association (CRIA). These agencies have been attacking such tracker websites as Bittorrent.com, Demonoide and ISOHunt among many others by subjecting them to raids and shutdowns due to claims of copyright infringement.
We have seen many of the bigger torrent sites shut down due to increasing pressures and threats of large fines to these companies. A recent turn of events in this matter is the case of a torrent site known as ISOHunt. In May of 2008 the site owners received what is known as a “cease and desist” letter from the CRIA which is a kind of threat to take their site offline. Instead of complying with these demands, ISOHunt decided to sue the CRIA saying they do not infringe on copyright laws. The hope of the site owners is that the CRIA will challenge this so that ISOHunt can prove their case and set a precedent for other bittorrent sites to be seen as legal.
There are no real guidelines set as of yet in the legal system that is based on precedent so it is a battle between the two sides to begin setting such precedents. ISOHunt is ultimately seeking validation of their site. It is their defense that the CRIF is going after the wrong people. Bittorrents do not store any copyright material they are simply a mechanism used to share data across the web. It will be up to the courts to decide whether Bittorrents are infringing upon copyright laws, or whether they are a legal form of search engine that inevitably can be used for illegal purposes that are out of their control.
The issue does not stop there, if the courts find Bittorrent sites guilty of aiding copyright infringements, can the blame then be passed to companies such as Microsoft for providing the computers to do such illegal activity, or to the internet companies such as Shaw who provide the internet services to users which in turn gives people access to the torrent sites? It will be up to the courts to decide.
BitTorrent Statistics
BitTorrent activity ccounts for about 35% of all traffic on the entire Internet.
The total amount of shared content is currently more than 1.1 petabytes (equal to one quadrillion bytes, or 10^15 bytes).
45 million people have downloaded this software to date. In addition Bit Torrent has an installed base of over 160 million clients.
Stats for ISOhunt:
Torrents: 19 987 / Trackers: 1057 / Seeds: 172875 / Leechers: 162073.
BitTorrent Clients
There are many clients for bitTorrent files, some of the common ones include:
Vuze
BitComet
BitTornado
Utorrent
FlashGet
Shareaza
Lime Wire
Best BitTorrent Sites
As of 2009, these are the five best torrent sites based on criteria such as the size of the database, readers' comments and feedback, the general trustworthiness of files, and more.
1.Demonoid
2.The Pirate Bay
3.Isohunt
4.Bitsoup
5.Torrentscan
Conclusion
Ever since BitTorrent emerged, it has changed the face of file distribution. Accessing TV shows, movies, music, and other files have never been as easy as it is now. Through this file-sharing technology, large corporations have lost billions of dollars in profits and the general population has the ability to choose whether they want to pay for their files or not. In the end, it is up to the individual to decide whether they want to utilize this technology or continue to buy their files by conventional means.
Resources
http://bits.blogs.nytimes.com/2008/09/04/comcast-appeals-fcc-sanction/?scp=bit%20torrent&st=search
http://www.codinghorror.com/blog/archives/000795.html
http://www.cbc.ca/nextprimeminister/blog/2008/03/canadas_next_great_prime_minis.html
http://netforbeginners.about.com/od/peersharing/f/torrentsearch.htm
http://www.theregister.co.uk/2004/12/14/mpaa_vs_bittorrent/
http://www.thewhir.com/web-hosting-news/kaye-debate
http://torrentfreak.com/bittorrent-more-popular-than-ever-071009/
http://torrentfreak.com/isohunt-sues-the-cria-to-legalize-bittorrent-sites-080905/
http://computer.howstuffworks.com/bittorrent2.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BitTorrent_(protocol)
http://isohunt.com/stats.php?mode=btSites
http://www.aarontoponce.org/presents/dvorak/images
http://www.nuc.berkeley.edu/courses/classes/E-124/Ethics%20in%20a%20Peer-to-Peer%20World.pdf