Courses/Computer Science/CPSC 203/CPSC 203 2007Fall L04/CPSC 203 2007Fall L04 TermProjects/Bits and Bytes
Contents
- 1 Project Information
- 2 Initial Project Statement
- 3 Introduction
- 4 Operation
- 5 Argument
- 6 A Brief History
- 7 Legal Issues
- 8 Advantages Compare to FastTrack
- 9 Disadvantages Compare to FastTrack
- 10 Formating Issues
- 11 Content Distribution
- 12 Network Impact
- 13 Security Concerns
- 14 Privacy Issues
- 15 Future of BitTorrent
- 16 Conclusion
- 17 References
Project Information
Team Name: Bits and Bytes
Group Members: Melanie McCann, Catherine Lawless, Mina Miyashita, Kiyeon Kang and Colton Kent
Team logo:

Initial Project Statement
Throughout this presentation Bits and Bytes will focus on peer to peer file sharing taking an in depth view at the intricacies within communications protocol. Furthermore, through the use of BitTorrent we will be able to examine the complexity of peer to peer file sharing. Moreover, we will provide you with insight into the vital role that BitTorrent plays in Internet technology as a main provider of links for many individuals. Therefore once this comprehensive presentation is complete you will be able to see how BitTorrent’s programs ultimately benefit consumers.
Introduction

BitTorrent was created by Bram Cohen in 2001. BitTorrent is an application of peer to peer file sharing, which acts as a large scale distributor of data. One of the main aspects of BitTorrent is the fact that one individual does not have to be responsible for the hardware involved, or hosting the set of data being transferred. As a result, each individual acts as a host distributing data to other individuals ultimately repeating the process until a peer to peer file sharing network has been established.
Brief Video Explanation:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=66BV2pIjfBM
Dowloading process
File downloading is processed between a client and a server. 
Vs. BitTorrents Peer to Peer Network Downloads:
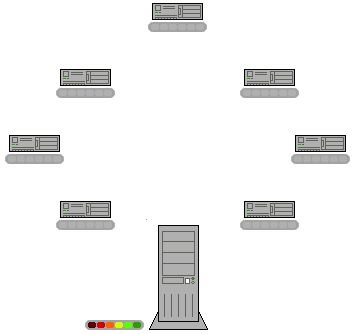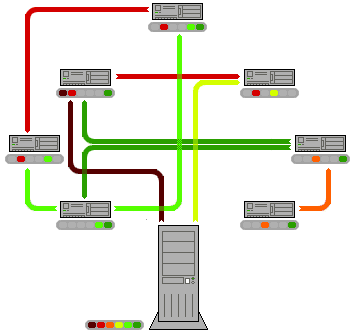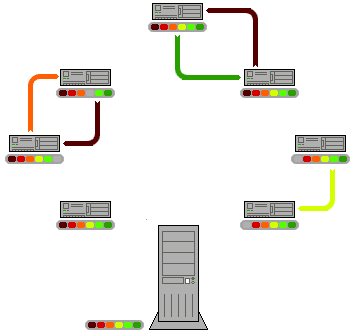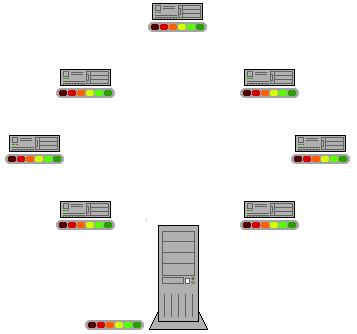 "In this animation, the colored bars beneath all of the clients represent individual pieces of the file. After the initial pieces transfer from the seed, the pieces are individually transferred from client to client. The original seeder only needs to send out one copy of the file for all the clients to receive a copy."[2]
"In this animation, the colored bars beneath all of the clients represent individual pieces of the file. After the initial pieces transfer from the seed, the pieces are individually transferred from client to client. The original seeder only needs to send out one copy of the file for all the clients to receive a copy."[2]
Operation
A BitTorrent client is any program that implements the BitTorrent protocol. Each client is capable of preparing, requesting, and transmitting any type of computer file over a network, using the protocol. A peer is any computer running an instance of a client.
To share a file or group of files, a peer first creates a "torrent". This small file contains metadata about the files to be shared and about the tracker, the computer that coordinates the file distribution. Peers that want to download the file first obtain a torrent file for it, and connect to the specified tracker, which tells them from which other peers to download the pieces of the file.
Though both ultimately transfer files over a network, a BitTorrent download differs from a classic full-file HTTP request in several fundamental ways:
BitTorrent makes many small P2P requests over different TCP sockets, while web-browsers typically make a single HTTP GET request over a single TCP socket. BitTorrent downloads in a random or in a "rarest-first"[2] approach that ensures high availability, while HTTP downloads in a sequential manner. Taken together, these differences allows BitTorrent to achieve much lower cost, much higher redundancy, and much greater resistance to abuse or to "flash crowds" than a regular HTTP server. However, this protection comes at a cost: downloads take time to rise to full speed because these many peer connections take time to establish, and it takes time for a node to get sufficient data to become an effective uploader. As such, a typical BitTorrent download will gradually rise to very high speeds, and then slowly fall back down toward the end of the download. This contrasts with an HTTP server that, while more vulnerable to overload and abuse, rises to full speed very quickly and maintains this speed throughout.
Key Terms Regarding BitTorrent:
- Swarm: Is a group of computers that are sending, uploading, receiving, or downloading the same file simultaneously.
- Leeches: Individuals who download files but do not complete the peer to peer network by sharing their own files with others.
- Seed: A seed refers to the computer which must hold a complete coopy of a BitTorrent file, while a "seeder" is the individual who holds that file. This operation must take place in order for a BitTorrent download to be sucessful.
- Tracker: A server that will manage and oversee the BitTorrent file transfering process.
- Torrent: A specific file that will dirrect your computer to the file you wish to download.
Argument
The influence of peer to peer networks is substantial. As a direct result, copious amounts of individuals are turning to BitTorrent to "use a secure, private, managed peer network to power faster delivery of richer content." With over 150 million users, BitTorrent is more than a stepping stone in software and content distribution. However, BitTorent has proven to be a controversial subject ranging from issues of ethics, to issues of whether other protocols such as Kazza are superior to BitTorrent. Despite the controversy, it is our belief that the advantages of using BitTorrent severely outweigh the disadvantages. Therefore, through the use of comparisons between Kazza and BitTorrent, relevant case studies of BitTorrent use, and by addressing a question of ethics, Bits and Bytes will arm you will the foreknowledge of the intricacies within BitTorrent, and why it ultimately benefits consumers like yourselves.
A Brief History
Bram Cohen - the cofounder of CodeCon, was the first to introduce the peer-to-peer protocol, BitTorrent. He began working on the project of BitTorrent on April 2001, and then, he started to collect free pornography from sites to use the program. By October 2002, people were able to share large music and movie files though the Internet for no charge and, BitTorrent gradually became popular to the fans of Japanese anime, as people were able to share foreign cartoons online.
Brief Video Explanation of BitTorrent's history:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lC7GIUobLlo

Bram Cohen and Fans
Legal Issues
BitTorrent trackers have been subjected to raids and shutdowns due to claims of copyright infringement. BitTorrent metafiles do not store copyrighted data, so it has been claimed that BitTorrent trackers, which only store and track the metafiles and usually do not share any potentially copyrighted data, must therefore be legal.
There are two major differences between BitTorrent and many other peer-to-peer file-trading systems, which advocates suggest make it less useful to those sharing copyrighted material without authorization. First, BitTorrent itself does not offer a search facility to find files by name. A user must find the initial torrent file by other means, such as a web search. Second, BitTorrent makes no attempt to conceal the host ultimately responsible for facilitating the sharing: a person who wishes to make a file available must run a tracker on a specific host or hosts and distribute the tracker address(es) in the torrent file. Because it is possible to operate a tracker on a server that is located in a jurisdiction where the copyright holder cannot take legal action, the protocol does offer some vulnerability that other protocols lack. It is far easier to request that the server's ISP shut down the site than it is to find and identify every user sharing a file on a peer-to-peer network. However, with the use of a distributed hash table (DHT), trackers are no longer required, though often used for client software that does not support DHT to connect to the stream.
BitTorrent is an example of the antagonism between "information gifts" and "information commodities" (Fuchs 2008). On the one hand there are people who think that knowledge should be free of charge and available to all, because it is part of the commons of society; on the other hand, there are people who argue that knowledge is an individual creation that should be individually owned, thus warranting protection under copyright law. These different attitudes result in social struggles in the online world.
Advantages Compare to FastTrack
Using bit torrent is advantageous compare to using Kazaa in many perspectives.
- Brief introduction to Kazaa and BitTorrent
Kazaa- A client can act as a server, leecher, or both. In other words, clients are downloading off other clients. A client acting as a server can decide which part of their hard drive will be shared. Once a server client decides which part of their hard drive will be shard, any clients can search the shared area and download as much as they want out of it.
BitTorrent- A client will search for a torrent via search engines such as google.com. Once they find a torrent that carries the desired file, the client will add the torrent on the bit torrent program and start downloading.
- Download speed
Kazaa- A client cannot download and upload a file at the same time. This means that until you have finished downloading a file, you cannot share it with others. 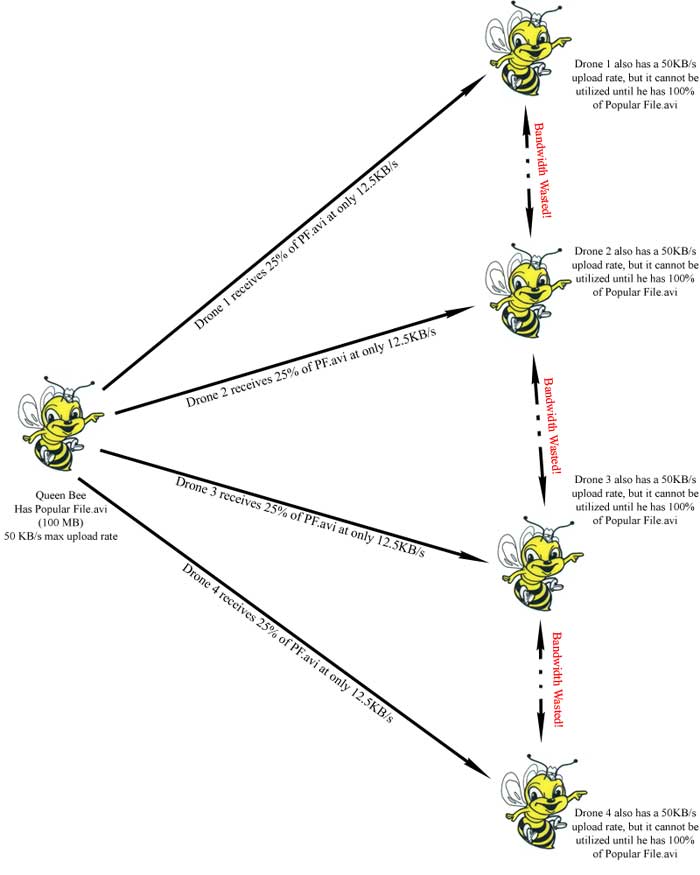
BitTorrent- A client CAN download and upload a file at the same time. This means that even if you are still downloading a file, you can share that file with others.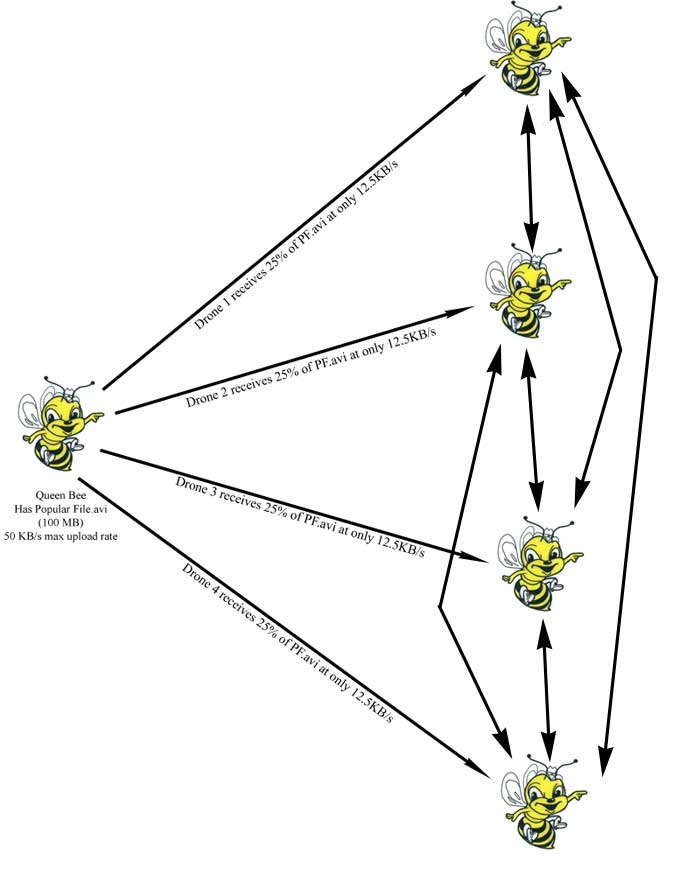
- New releases update
Kazaa- It takes a long time for a new released file to be shared. Some seeders will own the files, and there will be a humongous number of leechers demanding the files. In Kazaa, small number of seeders and large number of leechers means it will slow the download speed. Until the number of seeders grow, it will be very difficult to download new released files.
BitTorrent- A client can download new released files very quickly. Some seeders will own the files, and there will be numerous leechers demanding the files. In BitTorrent, large number of leechers means it will boost up the download speed. Sometimes, clients in West Coast can download television programs before the West Coast is even able to watch it on television(due to time zones).
- Virus
Kazaa- It is highly likely that clients have harmful viruses or spyware because they move with the files from computers to computers as the files transfer.
BitTorrent- Most of BitTorrent clients and servers do not contain viruses or spyware.
Disadvantages Compare to FastTrack
- Security
In many cases, peer to peer file sharing networks require users to create unique user names of their own. In the process of downloading, leechers and seeders would identify each other by their user names. However, unique user names are NOT required in the use of BitTorrent. Leechers and seeders know each other by their IP addresses. This means that your information, such as your location, is exposed to anyone who's sharing files with you.
- Limit on uploading amount
Most of home internet lines have limits on how much users can download or upload. Usually, people download much more than upload; therefore, the limitation on uploading is much smaller. In other words, you are allowed to upload only a little. The reason BitTorrent can be so much faster than FastTracks is because you upload at the same time you are downloading. Uploading amount will reach the maximum point in a little while. Users will have to get a bigger limit from the service provider which will cost more money.
- Lack of seeders for old files
Once seeders finish downloading, they will delete the torrent file from their computers. Consequently, number of seeders gradually decreases. As time passes, there will be only few or no seeders left. This means, it is difficult to download old files such as old movies.
Formating Issues
When downloading video files from torrent sites, often the format of the video file does not match Windows Media Player, QuickTime or other standard video players. This causes further downloading of programs that can read specific video files which causes a snowball effect creating a lot more free downloading. Solutions to this problem are video players which have the capability of playing multiple formats. A popular one of these players available to the public to download is DivX. It is capable of playing multiple video files and because it is a free program it does not break any copyright laws.
Content Distribution
Installation Instructions:
Step 1: Click the "Install DNA" button

Step 2: When prompted by these windows, click "Run".

Step 3: Click through the screens of the DNA Setup Wizard:

Congratulations, you have now completed the steps to install BitTorrent DNA. Now that wasn't so hard, was it!
BitTorrent's Entertainment Network
- In February of 2007, BitTorrent launched their "BitTorrent Entertainment Network" officially at BitTorrent.com. This newly founded network contains a expansive library of digital entertainment on the web that can be downloaded to BitTorrent's customers. The corporations BitTorrent is using by proxy for their entertainment expansion include 20th Century Fox, MTV Networks, Lions Gate, Paramount Pictures, Warner Brothers, and Metro Goldwyn-Mayer Studios, also known as (MGM). This announcement enables users to purchase television shows, music videos, and even rent movies with high quality content from the most infamous names in entertainment.

- BitTorrent's ability to produce high quality downloads is in part due to their partnership with 35 diverse content partners. When the entertainment network was launched in February of 2007, there was more than 5,000 movies, television shows, PC games, and music content available. Furthermore, there was also more than 40 hours of high definition programming available, a testament to the mere fact that BitTorrent comes updated with the latest technology, in any industry.
- As of February 2007 the movies that customers were able to enjoy include, Superman Returns, Mission Impossible III, Jackass: Number Two, An Inconvenient Truth, Napoleon Dynamite, Sideways, and The Thomas Crown Affair. With regards to television BitTorrent offered such hits as 24, Prison Break, My Super Sweet Sixteen, Celebrity Deathmatch, Muscle Car, South Park, Hogan Knows Best, and Spongebob Sqaurepants.

Pricing:
Though BitTorrent is able to process the latest hits from both television and the movie industry, an imperative question still remains for most customers, what will the cost to them be? Despite the comprehensive network BitTorrent holds, consumers may be surprised to learn the pricing model is fairly simple. Users can expect to see content that is free, some for rent, and some for purchase. The price for renting movies ranges from $2.99-$3.99, with $3.99 being the current price for new releases, which is in fact still better than your average video store. The price of downloading a Television show or music video to own is $1.99. Futhermore, an important point to note is that some of the content downloaded will be offered for free, without digital rights management (DRM). In essence this means that some of the content of BitTorrents Entertainment Network are free to download, without DRM, while some of the paid content has DRM to restrict copying.
How?
Now that we are aware of how expansive BitTorrent's network is, the underlying question of how BitTorrent is able to provide these services still remains. Below, we will address the details of BitTorrent's operations which include their DNA, and downloading options.

BitTorrent DNA:
Officially BitTorrent DNA stands for BitTorrent Delivery Network Accelerator. BitTorrent DNA provides users with a private and secure network. Through the utilization of BitTorrent DNA customers are able to download software, and have the ability to accelerate the use of streaming video files as well. More importantly, BitTorrent's DNA is able to work with your existing content delivery network, enabling a hassle free environment to pursue. This is primarily done by "distributing the end users downloads" between one another, therefore the content providers will not be bombarded with a large load on their servers, allowing the speed users receive to be more than optimal.
 BitTorrent DNA's managed peer network, seeded by CDN
[3]
BitTorrent DNA's managed peer network, seeded by CDN
[3]
Network Impact
- According to CableLabs, a non profit research and development organization BitTorrent represents 18% of all broadband traffic. However, in 2004 CacheLogic estimated that BitTorrent is responsible for 35% of internet traffic. The main reason for these discrepancies in measuring traffic include a difference in the methodology used in measuring peer to peer traffic on the internet.
Security Concerns
Most people think that it is easy to spread a virus through BitTorrent since, it is an application of Peer-to-Peer file sharing. However, it is extremely diffcult to transmit virus since BitTorrent users only transfer certain segements of the file, instead of the whole thing. In addition, users can’t transfer unknown files and, since it works in an open BitTorrent window, users cannot transfer anything outside of it, which makes it almost impossible to infect the file.
Users do not have to worry about security concerns while using BitTorrent however, there are some key factors to consider when using P2P networks:
1. Do not use P2P network on a corporate network.
2. Beware the client software.
3. Do not share everything with the users.
4. Scan your computer.
Details to each of the 4 key points listed above can be found here: (http://netsecurity.about.com/od/newsandeditorial1/a/p2psecurity.htm)
Privacy Issues
BitTorrent is committed to respecting the privacy rights and concerns of all users of our Sites and Services. As such, BitTorrent has established and implemented this privacy policy to inform visitors to the Sites and users of the Services how it uses and protects the information they collect.
You may visit the BitTorrent Features without any registration at all. However, from time to time, it may enable certain additional functionality to the BitTorrent Features, whereby you will have to create a user account. When you register and create an account, it may require you to provide your contact information including your name, address, phone number and e-mail address. Your user name and password will be used so you can securely access and maintain your account. BitTorrent may also use e-mail addresses and other personally identifiable information from time to time in order to gather and provide to its members and visitors improved content and features.It also keeps a record of your content downloads from BitTorrent.com and related transaction data, including payment information (if any).
BitTorrent implements a variety of security measures to ensure the security of your personal information on its systems. User personal information is contained behind secured networks and is only accessible by a limited number of employees who have special access rights to such systems. Any credit card information you supply us is transmitted and protected via Secure Socket Layer technology ("SSL") and HTTPS protocol and then encrypted into our databases to be accessed only as stated above.
BitTorrent does not currently sell, trade, or otherwise transfer outside the company personally identifiable information that visitors voluntarily provide in any registration. However, this data in an aggregate form without any personally identifiable information may be provided to other parties for marketing, advertising, or other uses. Should you change your mind about the information you've provided to BitTorrent, should you no longer wish to receive information from it, or should your information change, BitTorrent has provided a way for you to correct, update or remove the personal data you gave.
Finally, BitTorrent may disclose your personally identifiable information upon a transfer or sale to another entity of all or substantially all of their assets or equity securities or upon any other corporate reorganization.
Future of BitTorrent
Will BitTorrent be able to compete with similar companies in the future such as Tivo and other websites offreing similar services? Will individuals pay an all access fee to view content on the web? With all of the various free download programs on the market will BitTorrent be competitive in future markets? BitTorrent will soon be competing directly with cable and satellite companies. Although a fee may be instituted and required to use BitTorrent in the future, its simplicity of not needing to be connected to a cable or satellite network, as well as having an almost limitless number of different kinds of shows and music gives it a advantage over other companies. Tivo, future competition of BitTorrent, which requires a cable and can only record a show which is playing on television will have trouble keeping up to the with BitTorrent because it will not have as much appeal to individuals who demand a wide array of media all at the same time. When BitTorrent switches from a free download site to a pay per view site, consumers will be able to choose between a monthly all-access fee or an ala carte plan. Consumer's will not necessarily need a cable TV hookup, just broadband internet access. This gives BitTorrent a competitive edge and gives consumer's the option of being able to cancel their TV service to save money. A huge and unprecedented amount of content is available through BitTorrent, such as TV shows, movies, video blogs, music, and all sorts of media created by the public and then distributed. In the future, BitTorrent may be capable of becoming the number one distributor of multimedia content.
Conclusion
Based on the comprehensive analysis we have presented on BitTorrent, it is extremely evident to see that BitTorrent peer to peer network will only continue to strive in a world where technology is rapidly becoming an imperative device used in our daily routine. BitTorrent is a simple application to access, and comes with an extensive library of entertainment, and data to enable a secure interplay of communications between individuals. Therefore, in order to adequately keep the lines of communications open between individuals in such a high pace society, it is evident that BitTorrent is a consumers number one bet in communication protocol, providing linkage for many individuals today and in the days to come.
References
2. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BitTorrent
3. http://www.dessent.net/btfaq/
4. http://computer.howstuffworks.com/bittorrent.htm
5. http://compnetworking.about.com/od/bittorrent/qt/bittorrentports.htm
6. http://www.torrentguide.net/
7. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/6396733.stm
8. http://www.hollywoodreporter.com/hr/search/article_display.jsp?vnu_content_id=1000617772
9. http://www.vnunet.com/vnunet/news/2199413/bittorrent-konichiwa-japan
10. http://www.softdistrict.com/bittorrent-ties-up-with-brightcove.html
11. http://www.forbes.com/technology/2007/10/08/brightcove-fox-paramount-tech-cx_ag_1009bittorrent.html
12. http://lunapark6.com/bittorrent-dna-announced-pens-deal-with-brightcove.html
14. http://ntrg.cs.tcd.ie/undergrad/4ba2.05/group4/
15. http://filesharingplace.be/guides/bittorrent.php
16. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bram_Cohen
17. http://www.bittorrent.com/about
19. Christian Fuchs . 2008. Internet and Society: Social Theory in the Information Age. New York: Routledge.
20. http://www.bittorrent.com/about/press/bittorrent-inc-launches-the-bittorrent-entertainment-network
22. http://www.cachelogic.com/
23. http://tech.groups.yahoo.com/group/BitTorrentTalk/
24. http://btfaq.com/serve/cache/1.html
25. http://www.joestewart.org/p2p.html
26. http://www.broadbandinfo.com/broadband-connection/peer-to-peer/bit-torrent-security.html
27. http://www.webopedia.com/DidYouKnow/Internet/2005/peer_to_peer.asp
29. http://support.bittorrent.com/cgi-bin/bittorrent.cfg/php/enduser/std_alp.php
30. http://www.golgotha.net/node/36
31. http://www.torrentdirectory.org/articles/article-1.html
32. http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-bittorrent.htm
34. http://www.lokitorrent.com
36. http://pcwin.com/media/images/screen/73782-bittorrent_pro
37. http://www.theregister.co.uk/2007/03/02/bitttorrent_analysis/
38. http://torrentfreak.com/the-future-of-bittorrent-071113/
39. http://ezinearticles.com/?The-Future-of-BitTorrent&id=427410
40. http://www.collegian.psu.edu/archive/2005/02/02-01-05tdc/02-01-05dscihealth-column-02.asp
41. http://www.btnova.net/2007/11/leading-bittorrent-admins-discuss.html
42. http://netforbeginners.about.com/od/peersharing/a/torrenthandbook.htm
43. http://a.scarywater.net/torrent/clients/
44. http://torrentfreak.com/9-bittorrent-how-tos/
45. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/technology/4374222.stm
46. http://www.oldversion.com/program.php?n=bittorent
47. http://www.techcrunch.com/2006/11/29/bittorent-raises-25-million-bram-cohen-is-history/
48. http://wiki.theppn.org/index.php/BitTorrent_Tutorial
49. http://www.news.com/BitTorrent-to-open-digital-media-store/2100-1025_3-6161944.html
50. http://www.animenewsnetwork.com/news/2007-11-19/anime-torrent-users-reportedly-sent-notices-by-isps